Figure 9. Transcription activation of cpxP by protein acetylation: a model.
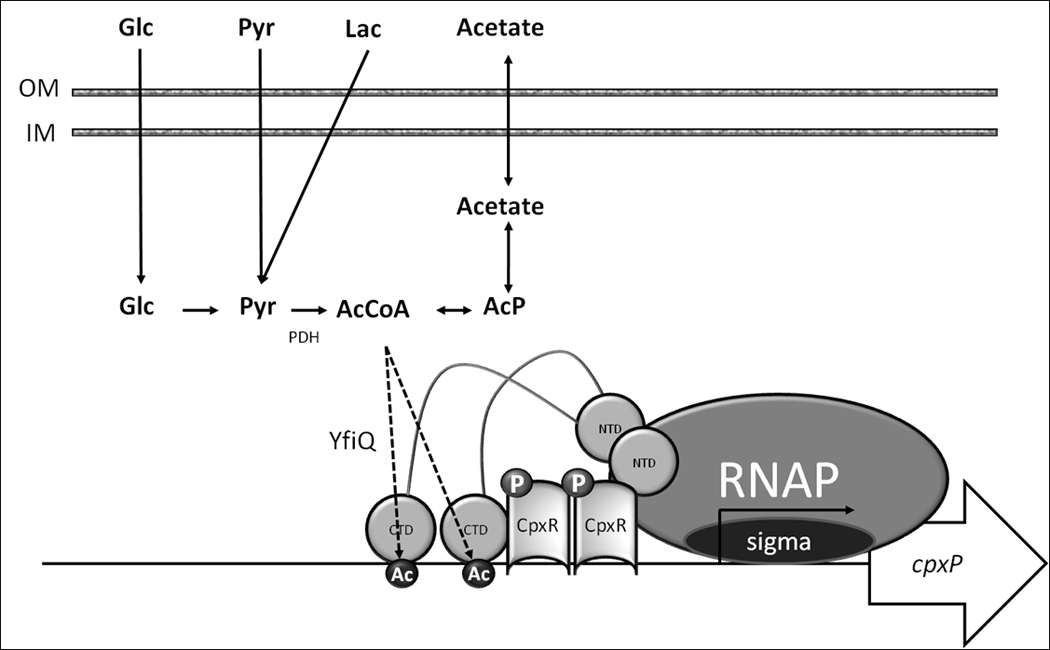
Glucose (Glc) and lactate (Lac) are converted to pyruvate (Pyr), which is converted to AcCoA by the enzyme complex pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH). AcCoA is interconverted with acetate by the Pta-Acka pathway, with acetyl phosphate (AcP) as an intermediate (Wolfe, 2005). AcCoA serves as an acetyl-donor to the acetyltransferase YfiQ, which is required for acetylation of several sites on RNAP, including K298 on α, which is required for CpxA-independent activation of cpxP transcription.
