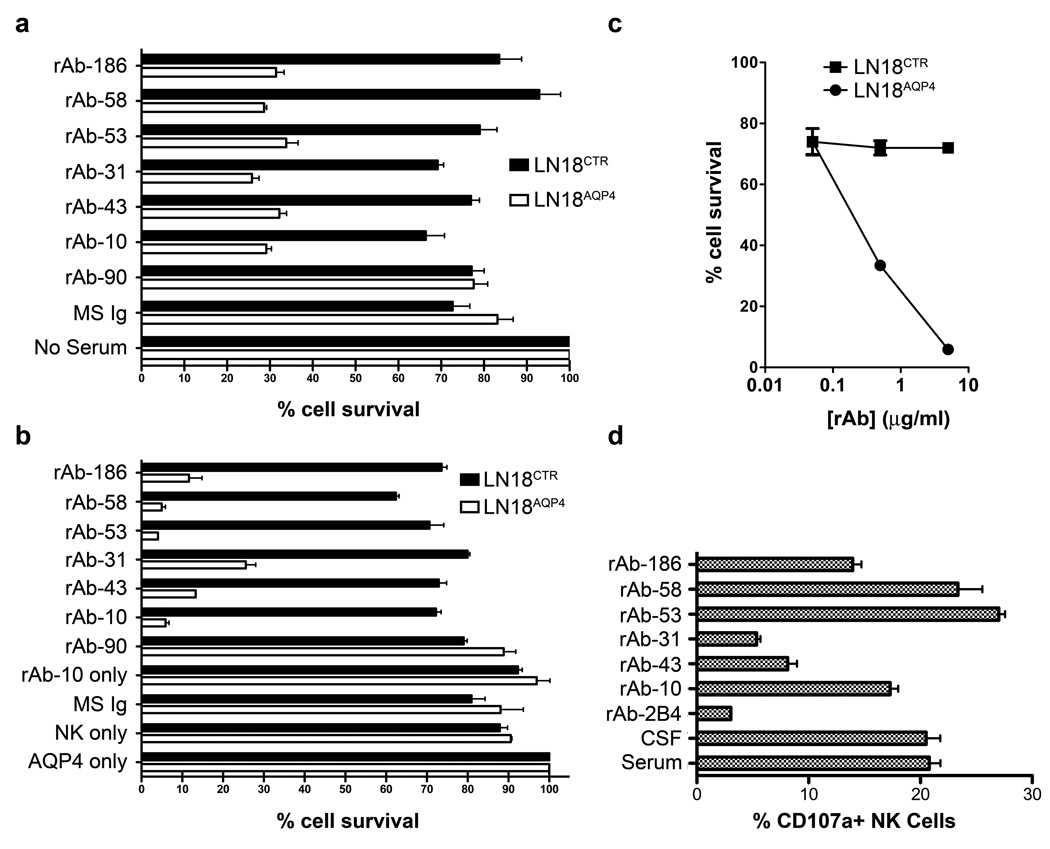
Fig 5.
AQP4-specific CSF rAbs are functional IgG1 antibodies. (A) AQP4-specific complement-mediated killing of LN18AQP4 and LN18CTR cells by CSF rAbs was quantitated using FACS analysis. The experiment was performed in duplicate, and the percentage cell survival was normalized to the negative control (No Serum) sample. The loss of LN18AQP4 cell viability was greater than 75% in the presence of AQP4-specific rAb (rAbs-10, -31, -43, -53, -58, and -186) and complement. Non-specific reduction in cell viability rarely exceeded 20% in the absence of serum (No Serum) or the presence of nonspecific serum (MS Ig) or CSF rAb (rAb-90). Mean and standard deviation are shown. (B) The induction of antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) of LN18AQP4 and LN18CTR cells in the presence of human NK cells and CSF rAbs was evaluated by FACS analysis. After 12 hrs of cocultivation, the number of viable LN18 cells in culture was quantitated and normalized to the number of surviving cells in the negative control (AQP4 only) sample that contained NMO patient serum in the absence of human NK cells. AQP4-specific rAbs-10, -53, and -58 resulted in a specific loss of more than 94% of the target LN18AQP4 cells; AQP4-specific rAbs-43, -186, and -31 caused a slightly lower amount of LN18AQP4-specific target cell death. No impact on LN18AQP4 cell survival was observed in the absence of rAb (NK only), the absence of NK cells (rAb-10 only), the presence of nonspecific serum (MS Ig) or CSF rAb (rAb-90). The experiment was performed in duplicates; mean and standard deviation are shown. (C) Serial dilution of CSF rAb-10 demonstrates that NK-mediated lysis of LN18AQP4 cells is dose dependent. AQP4-specific rAb-10 (5 µg/ml, 0,5 µg/ml and 0,05 µg/ml) was preincubated with either LN18AQP4 or LN18CTR target cells and the level of ADCC in the presence of human NK cells was quantitated by FACS analysis. Cell survival was determined after 10 hr cocultivation and normalized to the negative control (LN18CTR) cell line. (D) NK cell surface mobilization of CD107a was quantified by FACS analysis after coincubation of HFAs with NMO patient serum, NMO patient CSF, or AQP4-specific NMO CSF rAb. NMO patient serum, NMO patient CSF, and AQP4-specific CSF rAbs-10, --53, -58, and -186 resulted in comparable elevations in CD107a surface expression on human NK cells. CSF rAbs-43 and -31 triggered only modest CD107a surface mobilization compared to a measles virus nucleocapsid-specific control rAb (rAb-2B4). The experiment was performed in duplicates; mean and standard deviation are shown.