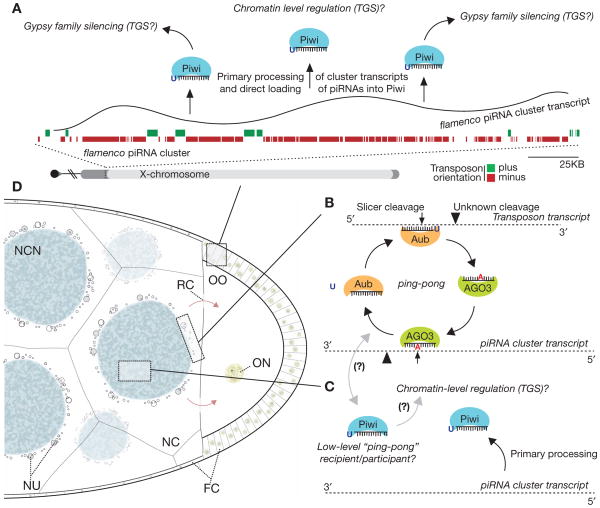
Figure 2.
Models of piRNA pathway silencing in distinct tissues of the Drosophila ovary. Germline and somatic cells of the Drosophila ovary use vastly different mechanisms to combat particular transposon threats. (A) In somatic cells of the ovary, flamenco cluster transcription precedes its processing to piRNAs that are directly loaded into the Piwi protein, which targets somatically expressed transposons (gypsy family) for silencing. Given Piwi’s nuclear localization, regulation is likely occurring at the transcriptional level. (TGS) Transcriptional gene silencing. (B) The Aub and AGO3 proteins actively cycle in a germline-specific feed forward amplification loop to generate a potent and abundant pool of silencing-capable piRNAs. (C) Piwi may act similarly in the germline as in the soma. Here, the Piwi protein may directly bind antisense, cluster-derived piRNAs to silence elements by TGS. Additionally, Piwi may serve as a low-level recipient or participant with AGO3 in the ping-pong cycle. (D) Diagram of a mid/late-stage egg chamber of the Drosophila ovary. (NC) Nurse cell (germline); (NCN) nurse cell nucleus; (OO) oocyte; (ON) oocyte nucleus; (NU) nuage; (FC) follicular cell (somatic); (RC) ring canal.