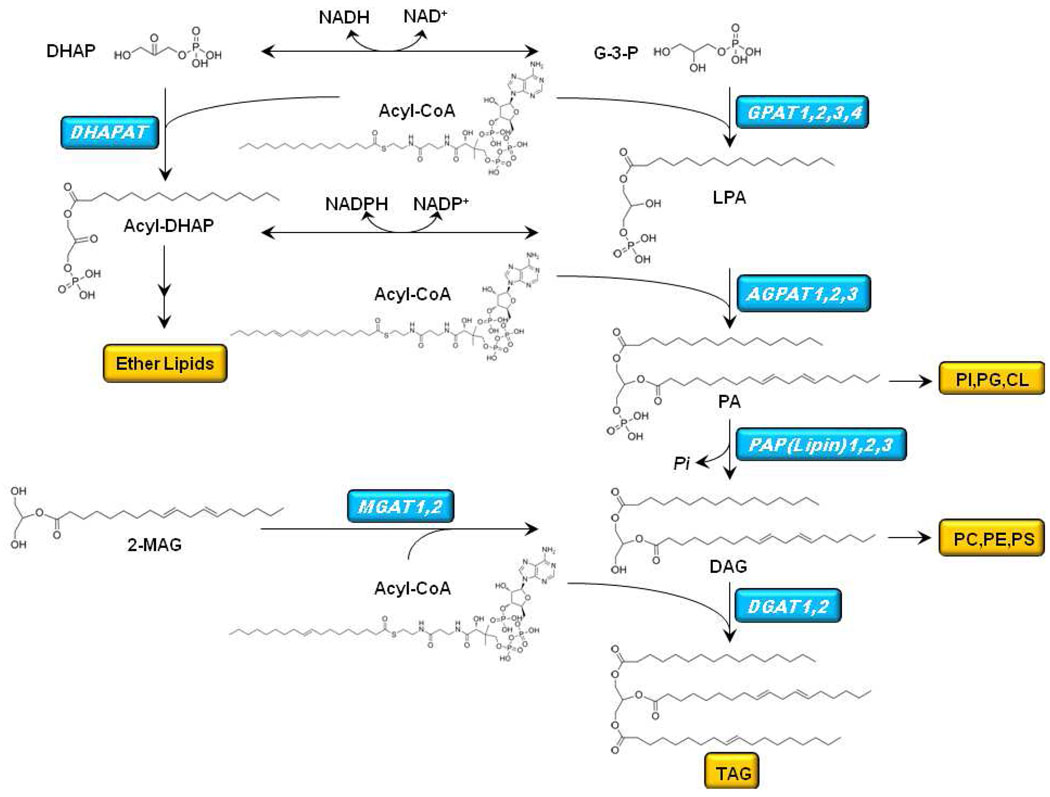
Figure 1. Pathway of glycerolipid synthesis.
The biosynthesis of TAG begins with the sequential acylation of glycerol-3-phosphate (G-3-P) by sn-1-glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase (GPAT) to produce lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) and by acyl-CoA:1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase (AGPAT) to produce phosphatidic acid (PA). G-3-P can also be produced by the oxidation of dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP), and the oxidation of acyl-DHAP produces LPA. PA is hydrolyzed by PA phosphatase (also called lipin) to form diacylglycerol (DAG). A final esterification step by DAG acyltransferase (DGAT) produces triacylglycerol (TAG). PA is also a precursor of CDP-diacylglycerol and the anionic phospholipids phosphatidylglycerol (PG), phosphatidylinositol (PI), and cardiolipin (CL). DAG is a precursor of the phospholipids, phosphatidylcholine (PC), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), and phosphatidylserine (PS). Acyl-DHAP is the precursor of the ether lipids.