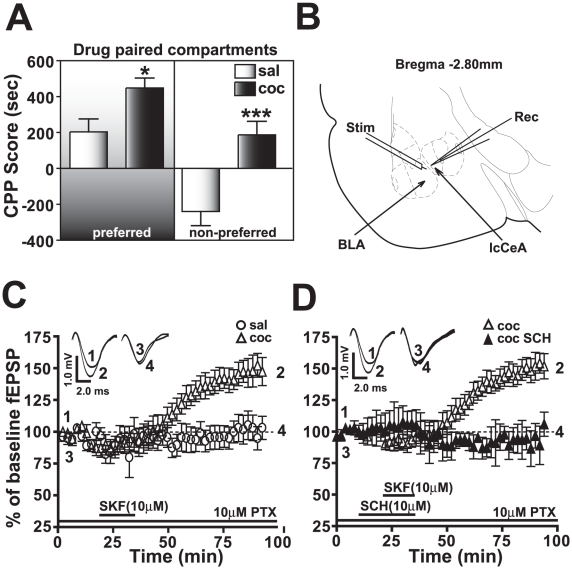
Figure 1. Amygdala slices (B) from animals exhibiting robust cocaine CPP (A) measured 14 days after the last day of CPP training demonstrate a D1/5R agonist-induced LTP in the BLA-lcCeA pathway (C) which is abolished by D1/5R antagonist application (D).
A) The cocaine CPP group (black bars) had significantly greater CPP scores than saline-treated animals (white bars) irrespective of whether the drug pairing was on the preferred (saline: 187.1±75.1, cocaine: 448.2±55.7, *p<0.05, n = 34) or the non-preferred side (saline: −239.7±78.5, cocaine: 203.8±71.7, ***p<0.005, n = 34). B) Placement of recording (Rec) and stimulating (Stim) electrodes are indicated in a schematic representation of the slice containing BLA-lcCeA pathway using a rat brain atlas template [127]. C) D1/5R agonist (SKF81297) induces LTP in the BLA-lcCeA pathway in brain slices from animals conditioned to cocaine and tested two weeks after the last CPP training day (clear triangles, 151.4±8.8%, *p<0.05, n = 6). The saline-treated group did not show potentiation (clear circles, 101.6±9.7%, ns, n = 7). Responses are plotted as percent change from the baseline field EPSPs as a function of time. Numbers on the representative traces show the time on the graph at which they were recorded. D) SKF81297-induced LTP in the amygdala from slices of cocaine CPP animals (clear triangles) is completely abolished by the D1/5R antagonist, SCH23390 (filled triangles, 94.5±10.9%, **p<0.01, n = 4). Significance is denoted by increasing number of asterisks (*). For comparison panels C and D use same data graphs and fEPSP traces for the slices from cocaine CPP group superfused with SKF81297.