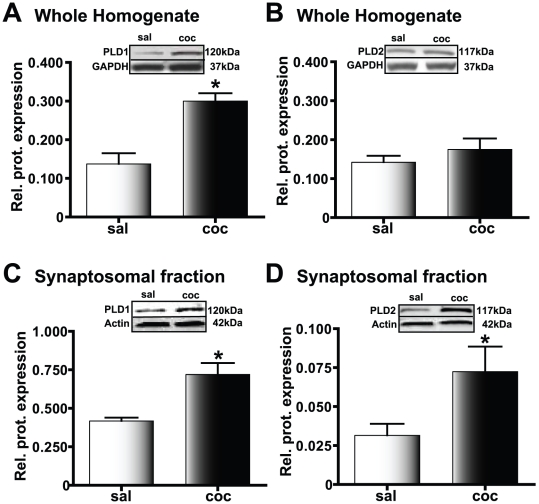
Figure 5. PLD levels in the amygdala are increased in cocaine CPP animals.
Protein expression relative to the loading control is plotted along the Y-axis. Representative immunoblots are shown in the panels above each graph; *p<0.05 compared to the corresponding saline-treated control. A) PLD1 levels in the whole amygdala homogenate are significantly increased in cocaine CPP animals (black bars) compared to the saline-treated group (white bars). B) PLD2 levels in the whole amygdala homogenate are not increased in the cocaine CPP group (black bars) compared to the saline-treated group (white bars). C) In the amygdala crude synaptosomal fraction, PLD1 protein levels are increased in the cocaine CPP group (black bars) suggesting that there is increased synaptosomal membrane incorporation of PLD1 in this experimental group compared to the saline-treated group (white bars). D) Similar to PLD1, amygdala crude synaptosomal levels of PLD2 show an increase in the cocaine CPP group (black bars). However, such increased expression is observed despite a lack of increase in the whole homogenate levels, suggesting that recruitment from the existing pool of PLD2 to the synaptosomal membrane is increased in the cocaine CPP group.