Figure 4.
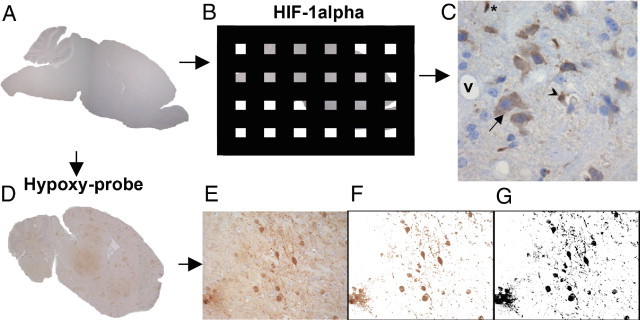
Approaches to assessment of tissue hypoxia. A: Tissue was cut in sagittal sections. B: For HIF-1α, the fractionator principle was applied, only counting cells in a predetermined fraction of the tissue. C: Each micrograph was assessed for HIF-1α expression, and the cellular subset was noted. V indicates the vessel lumen, and nucleated cells trapped intravascularly were noted for being HIF-1α–positive, if observed. Asterisk indicates a glial cell, arrowhead denotes an endothelial cell, and arrow indicates a neuron. D: For pimonidazole reactivity, a multifocal staining pattern was observed in CM mice. To assess the degree of hypoxia in each region of interest (E), the image was color thresholded (F) and converted to a binary image (G).
