Figure 4.
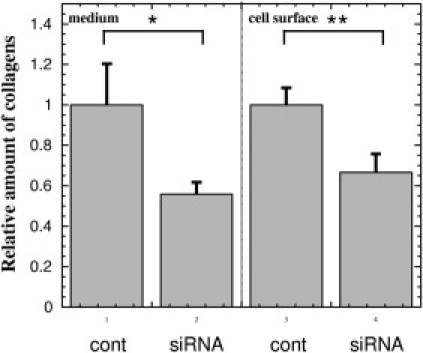
Suppression of cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP) by small interfering RNA (siRNA) reduces collagens in the culture medium of keloid fibroblasts and deposited on the cell surfaces. At 24 hours after transfection of the control (lanes 1 and 3) and COMP siRNA (lanes 2 and 4) into the subconfluent keloid-derived fibroblasts (KDFs) at 6-well plates, we put 1 mL fresh Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM) (Nissui Pharmaceutical, Tokyo, Japan) supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum containing 50 mg/mL ascorbic acid. For assay of collagen amount, at 72 hours after the medium change, the conditioned media (lanes 1 and 2) were subjected to the Sircol Collagen Assay Kit (Biocolor Ltd., Carrickfergus, UK) to measure type I to V collagens. Briefly, 1 mL of conditioned media were mixed with 200 mL isolation and concentration reagent in the kit and incubated at 4°C overnight. After centrifugation, pellets were re-dissolved in 1 mL of Sircol dye reagent (Biocolor Ltd.). After centrifugation, pellets were suspended in 1 mL of the alkali compound and collagen concentration was determined by spectrophotometric absorbance at 540 nm. After aspiration of the culture supernatant, extracellular matrix formed on the cells was treated with 1 mL 0.5 M cold acetic acid for 24 hours and the amount of collagens in the extract was determined with the Sircol Collagen Assay Kit (lanes 3 and 4). The amounts of collagens were determined using the KDFs from three different patients (n = 3) and expressed as relatives of each control transfected with the negative control siRNA (lanes 1 and 3). Statistical difference was determined by the Student's t-test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, cont, negative control siRNA.
