Figure 2.
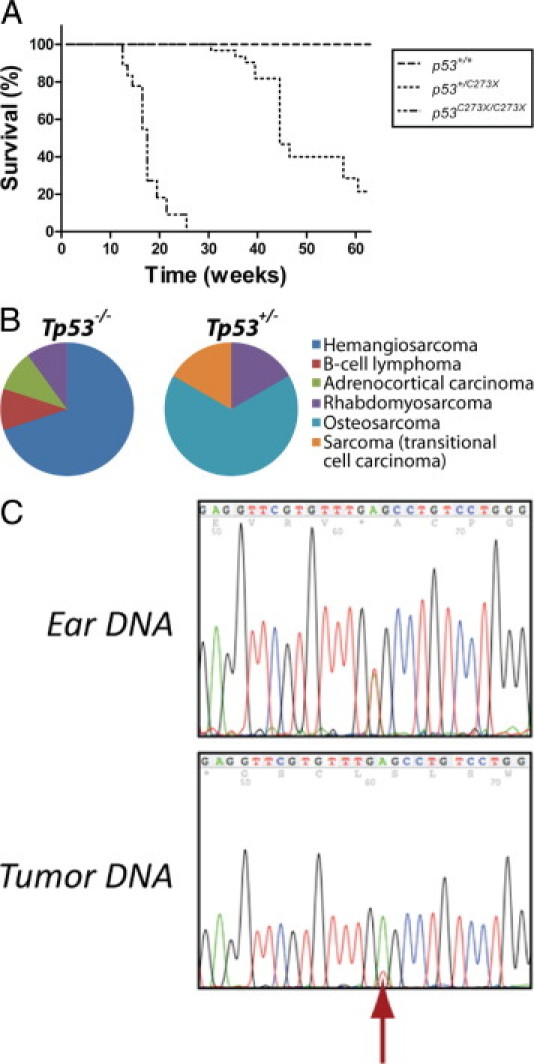
Tp53C273X mutant rats demonstrate a decrease in survival as a result of spontaneous tumor development. A: Homozygous mutant animals (n = 11) have sudden mortality at the age of 4 months, whereas a prolonged survival is observed in heterozygous carriers (n = 8) that reveals a median survival of approximately 9 months. No wild-type littermates (n = 4) became moribund during this study. B: Pie charts of the tumor types identified in homozygous (Tp53−/−) and heterozygous (Tp53+/−) mutant animals. C: Tumors in heterozygous (Tp53+/−) mutant rats display loss of heterozygosity of the wild-type Tp53 allele (red arrow). Sequencing analysis of DNA isolated from the ear revealed that the animals were heterozygous carriers of the Tp53C273X allele; however, loss of the wild-type allele was observed in tumor tissue.
