Figure 1.
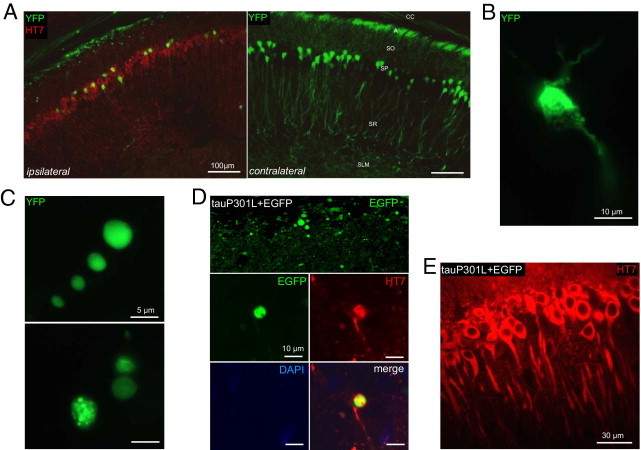
Tau damages dendrites and axons of CA1 neurons. A: YFP-expressing transgenic mice (n = 6) were analyzed to visualize degenerating neuritic processes. At 21 days after infection, AAV-tauP301L induced loss of apical and proximal dendrites and a significant decrease in the number of pyramidal neurons.1 Immunofluorescent staining was performed using HT7-bio and Strepta-Alexa 594 (red). A, alveus; SLM, stratum lacunosum moleculare; SO, stratum oriens; SP, stratum pyramidale; SR, stratum radiatum. B: Degenerating neuron in the CA1 of mouse injected with AAV-tauP301L. Note shrinkage and fragmentation of cytoplasmic YFP signal. C: Examples of YFP-positive dilatations in the alveus in YFP-expressing mice injected with AAV-tauP301L. YFP signal appeared as punctate (upper panel) or smooth (lower panel). D: WT mice were co-injected with AAV-tauP301L (10E8 t.u.) and AAV-EGFP (10E8 t.u.) (n = 5) or injected only with AAV-EGFP (10E8 t.u.) (n = 4). Images were obtained in the CA1 from 40-μm thick sections using a microscope (Leica Microsystems GmbH, Wetzlar, Germany). Tau-induced degeneration was associated with deposition of EGFP in dilatations in alveus similarly as in YFP-expressing mice. E: Neurons co-injected with tauP301L and EGFP express tau (HT7 staining) in the somatodendritic compartment.
