Figure 7.
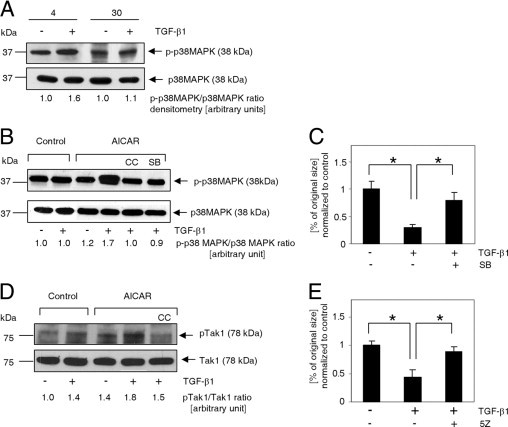
p38MAPK and Tak1 kinases are involved in TGF-β1/AICAR-dependent signal amplification. A: Immunoblot analysis of p38MAPK phosphorylation (Thr180/Thr182) in response to 30 minutes of activation with 10 ng/mL TGF-β1 in cardiac fibroblasts isolated from young (4 months old) and aged (30 months old) mice. B: p38MAPK activation depends on synergistic action of TGF-β1 and AICAR. Cells were exposed to AICAR (0.5 mmol/L) or TGF-β1 (10 ng/mL) for 1 hour. C: p38MAPK inhibition reduces collagen lattice contraction (free-floating collagen gel model). Cells were cultured in the presence of 0.5 mmol/L AICAR. At 72 hours before assay, cells were passaged, and the medium was supplemented with 10 ng/mL TGF-β1 and 20 μmol/L SB203580, as indicated. Collagen disks were incubated in serum-free medium for 24 hours. D: Tak1 phosphorylation (Thr184/Thr187) was enhanced via simultaneous application of AICAR and TGF-β1. E: Tak1 inhibition eradicated the ability of myofibroblasts to contract a collagen pad. Cells were cultured in the presence of 0.5 mmol/L AICAR. At 72 hours before assay, cells were passaged, and medium was supplemented with 10 ng/mL TGF-β1 and 100 nmol/L (5Z)−7-oxozeaenol, as indicated. Collagen matrices were incubated for 24 hours under serum-free conditions. B–E: Cells were derived only from 30-month-old animals. For Western blot analysis, cells were pretreated with inhibitors for 30 minutes before application of AICAR or TGF-β1. For collagen pad contraction, the medium was supplemented with inhibitors every 24 hours. CC, Compound C; SB, SB203580; 5Z, (5Z)−7-oxozeaenol.
