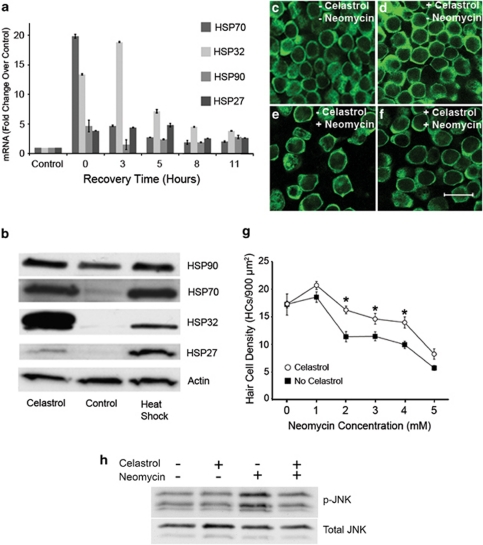
Figure 1.
Celastrol induces HSPs and inhibits aminoglycoside-induced hair cell death. (a) RT-PCR analysis of HSP mRNA expression. Utricles were treated with (or without) celastrol for 3 h and allowed to recover for 0–11 h. Celastrol resulted in robust upregulation of HSP70 and HSP32/HO-1 mRNA levels relative to control utricles. More modest upregulation of HSP90 and HSP27 mRNA were observed with celastrol. Error bars represent S.E.M. on real-time qRT-PCRs performed in triplicate. (b) Western blot analysis of celastrol-mediated HSP induction. Utricles treated with a 43°C heat shock were used for comparison. Celastrol induced HSP70 expression levels that were comparable to those induced by heat shock. Celastrol-mediated HSP32 induction was greater than that induced by heat shock. (c and g) Celastrol inhibits aminoglycoside-induced hair cell death. (c) Control utricles display normal hair cell densities. (d) Celastrol does not decrease hair cell viability. (e) Neomycin results in a significant loss of hair cells. (f) Celastrol inhibits neomycin-induced hair cell death. (g) Celastrol inhibits neomycin-induced hair cell death across the dose–response relationship (2-way ANOVA F1,132=28.916, P<0.001). (h) Celastrol inhibits aminoglycoside-induced JNK activation. JNK activation was analyzed by phosphorylation status. Celastrol (1.5 μM for 3 h) does not result in JNK activation. Neomycin resulted in robust JNK activation relative to basal levels. Neomycin-induced JNK activation is inhibited by celastrol. Scale bar in f=20 μM. Asterisks in g denote a significant difference in neomycin-induced hair cell death between celastrol-treated and untreated utricles by post hoc tests