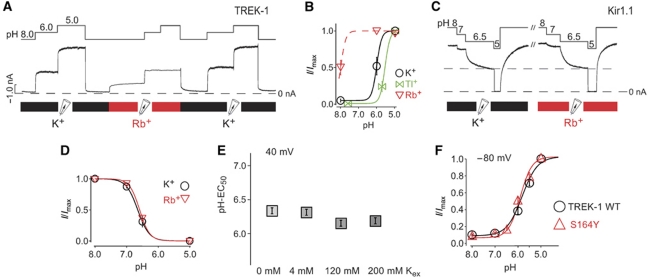
Figure 8.
Effect of permeant ions on TREK-1 activation by pH. (A) pH activation of TREK-1 channels in the presence of Rb+ in comparison with K+ as permeating ion, measured at 40 mV. (B) Dose–response curves from experiments such as in (A) for different ionic species indicating a large effect of the permeant ion on pH activation in TREK-1 channels (n⩾4 for each ion). (C) pH sensitivity of Kir1.1 in the presence of K+ and Rb+ as the conducting ion. (D) Dose–response curves from experiments such as in (C) fitted with standard Hill equation resulted in pH0.5=6.62±0.068 for K+ (n=6) and 6.58±0.017 for Rb+ (n=8). (E) No effect of external [K+] concentration on the EC50 for pH activation in TREK-1 channels (n⩾6 for each [K+] concentration). (F) Comparison of pH activation in TREK-1 WT (EC50=5.9±0.1; n=9) versus S164Y mutant channels (EC50=6.0±0.1; n=6) (a mutation related to extracellular pH sensitivity; Cohen et al, 2008) indicating no effect of this mutation on intracellular pH sensitivity.