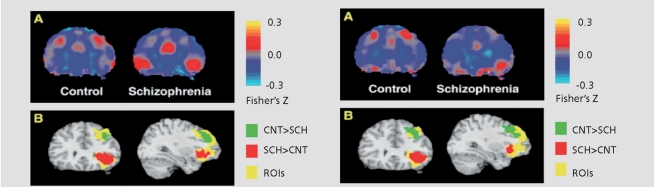
Figure 3.
Group differences in left STG-DLPFC and STG-VLPFC connectivity (Left Column) and in left PHIP-DLPFC and PHIP-VLPFC connectivity (right column). For the left column, panel A: group-averaged STG timeseries correlation maps for control group (left) and schizophrenia group (right), from a representative coronal plane (y = 30). A region of DLPFC shows greater connectivity (measured as average Fisher's Z-transformed correlation coefficients) with STG in controls, while a region in VLPFC shows greater connectivity with STG in patients. Panel B results of voxel-by-voxel t-tests are overlaid on the two prefrontal regions of interest and a standard reference brain (Colin, MNI), in the same coronal plane. The group differences seen within DLPFC and VLPFC are statistically significant. For the right column, Panel A: groupaveraged PHIP timeseries correlation maps reveal a region within DLPFC showing greater connectivity with PHIP in controls, while a region within VLPFC shows greater connectivity with PHIP in patients. Panel B: group differences seen within DLPFC and VLPFC are statistically significant. STG, superior temporal gyrus; DLPFC, dorsolateral prefrontal cortex; VLPFC, ventrolateral prefrontal cortex; PHIP, parahippocampal gyrus; CNT, control; SCH, schizophrenia; ROI, region of interest.
Reprinted with permission from ref 1 3: Gur RE, Turetsky BI, Loughead J, et al. Visual attention circuitry in schizophrenia investigated with oddball event-related functional magnetic resonance imaging. Am J Psychiatry. 2007;164:442-449. Copyright © American Psychiatric Association 2007