Figure 5.
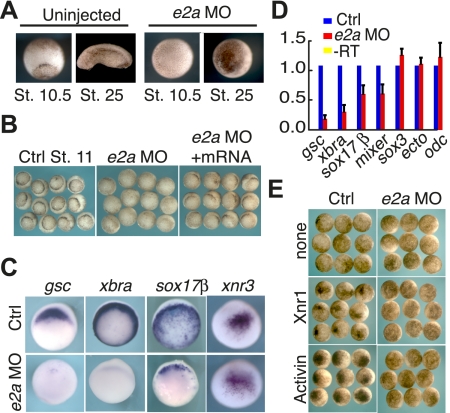
E2A is essential for gastrulation and gene expression in X. tropicalis. (A, right) X. tropicalis embryos were injected with a translation-blocking MO (e2a MO) directed against e2a, and assayed morphologically at stages 10.5 and 25. These were compared with uninjected controls (shown at left). (B) Blastopore lip formation in e2a MO-injected embryos can be restored by subsequent injection of mouse e2a mRNA. Using either in situ hybridization (C) or qRT–PCR (D), e2a MO-injected embryos were compared with controls for expression of molecular markers. qRT–PCR results represent at least four biological replicates. (E) e2a morphants and uninjected controls were injected in the animal pole at the four-cell stage with 10 pg of Activin mRNA or 40 pg of Xnr1 mRNA, and assayed for the presence of ectopic bottle cells. Representative embryos are shown at stage 11 in animal views.