Table 1.
Intermolecular C—H Esterification with Homoallylic Oxygen Substitution
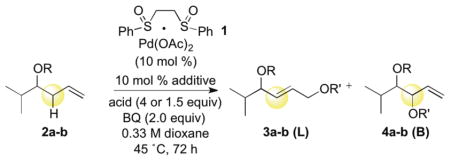 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry | R | R′a | additive | isolated yieldb | L:Bc 3/4 | E:Z (3)d | dr (4)e |
| 1 | CH2CO2Me | Ac | none | 11 | 1:2 | >20:1 | 16:1 |
| 2 | CH2CO2Me | Ac | Cr(salen)Cl | 10 | >20:1 | >20:1 | N/A |
| 3 | CH2CO2Me | p-NO2Bz | none | 16 | 1:2 | nd | >20:1 |
| 4 | CH2CO2Me | p-NO2Bz | Cr(salen)Cl | >5 | nd | nd | nd |
| 5 | Bn | p-NO2Bz | none | >5 | nd | nd | nd |
AcOH (4.0 equiv) or p-NO2BzOH (1.5 equiv) used as the acid nucleophile.
Average of 2 runs at 0.5 mmol.
Linear(L):Branched(B) ratio determined by GC of the crude reaction after workup.
E:Z ratio determined by GC of the crude reaction after workup.
Diastereomeric ratio determined by GC of the crude reaction after workup. BQ = p-benzoquinone, salen = 1,2-cyclohexanediamine-N, N′-bis(3,5-di-tert-butylsalicylidine).
