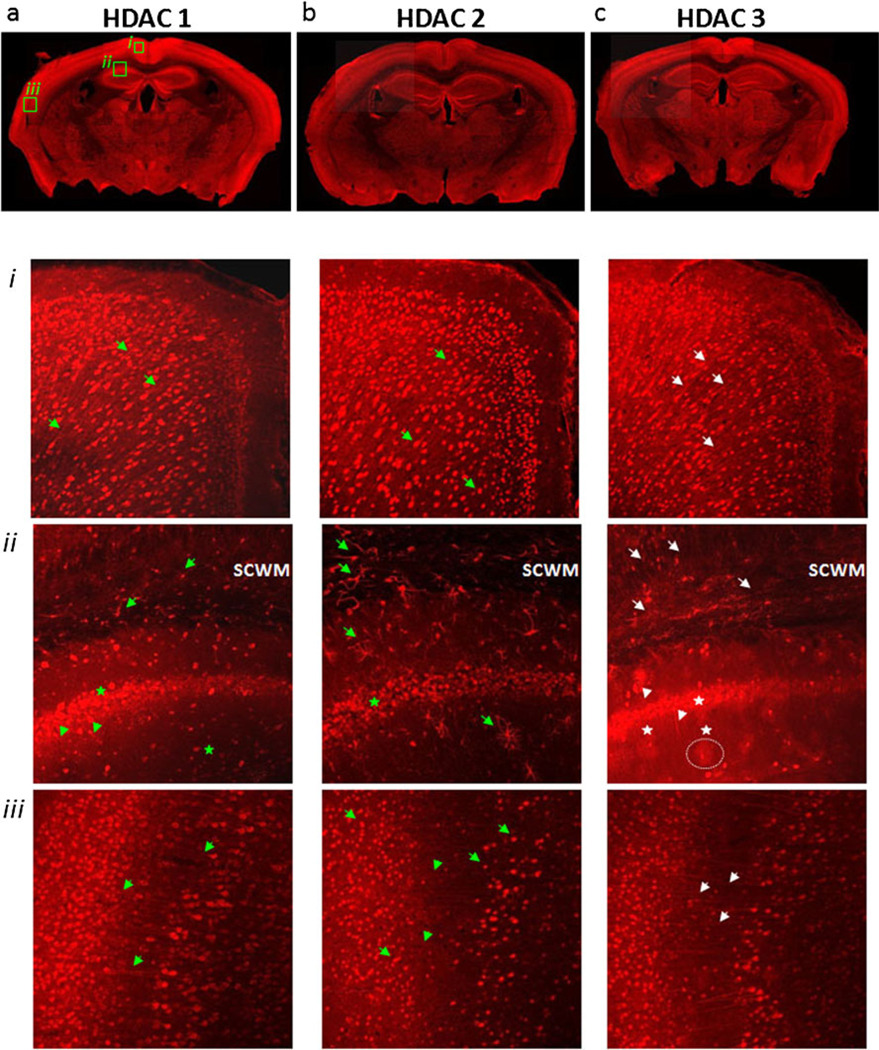
Fig. 1.
Class 1 HDAC expression in the adult mouse brain. HDACs 1 (a), 2 (b), and 3 (c) are highly expressed in cortical and hippocampal neurons, with relative detection decreasing in other neuronal cells away from the cortex and low expression in areas of white matter. a In cingular (i) and parietal (iii) cortex, HDAC 1 expression was in neuronal cell bodies and in their axons. In hippocampal CA1–CA2 junction (ii), HDAC 1 expression was prominent in pyramidal cell bodies (stars) and was visible in some dendrites (arrowheads). In overlying subcortical white matter (SCWM), HDAC 1 expression was present in some nuclei and associated processes (arrows). b HDAC 2 expression was localized to neuronal nuclei in cingulate (i) and parietal cortex (iii) (arrows) and hippocampal pyramidal cells (ii) (stars). In some sections of the parietal cortex (iii), HDAC 2 labeling was faintly visible in axons (arrowheads). HDAC 2 expression was very prominent in SCWM and hippocampus (ii) in some astroglial nuclei and uniformly outlining their associated processes (arrows). c HDAC 3 was expressed in the nuclei of neurons and axons in cingulate and parietal cortex (i and iii) (arrows), but in the cytoplasm of pyramidal neurons of the hippocampus (stars), as well as in their axons and dendrites (ii) (arrowheads). Note HDAC 3 nuclear labeling associated with the synaptic domains of interneurons away from the pyramidal cell layer (dotted line)