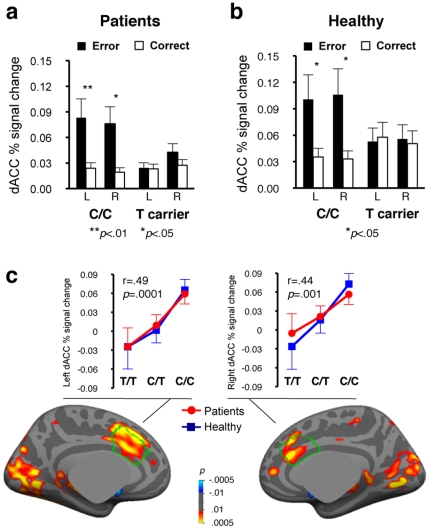
Figure 2. Effects of MTHFR 677C>T genotype on error-related dACC activation.
Both schizophrenia patients (a) and healthy participants (b) exhibited significant condition×genotype interactions (patients: F = 4.51, p = .042; healthy participants: F = 10.32, p = .004) indicating that C/C participants, but not T allele carriers, showed significant error-related dACC activation. (c) Pseudocolor statistical maps of the relationship between 677C allele load (0, 1, or 2 copies) and error-related activation (error minus correct) in the combined group, displayed on the inflated medial cortical surface. The dACC is outlined in green. Graphs illustrate the effects of allele load on error-related activation, averaged across vertices in the anatomically defined dACC, for patients and healthy participants. Error bars indicate the standard error of the mean.