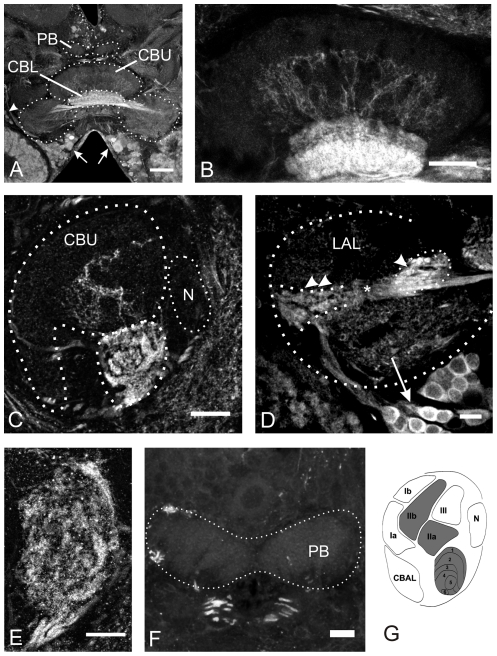
Figure 3. GABA immunoreactivity in the central complex.
A and B: Frontal sections through the midbrain (A) and the central body (B). The entire lower division (CBL) is densely innervated by GABA positive neurites, while only few neurites in the upper division (CBU) contain GABA. The somata of these fibers are located in the inferior-median protocerebrum (arrows in A and D) and in the inferior lateral protocerebrum (arrowhead in A). C and E: Sagittal sections through the central body. Staining in the CBU is restricted to layer II, while the other layers are devoid of GABA. The CBL is densely innervated by GABA-containing neurites. GABA positive fibers enter the CB via the posterior groove. D: Frontal section through one lateral accessory lobe (LAL). Fibers originating from cells in the inferior median protocerebrum run through the isthmus tract (indicated by asterisk) before they enter the CB. Knob-like staining is observed in the lateral triangle (double arrowheads). Additional intensive immunoreactivity is present in the median olive (arrowhead). F: Frontal section through the protocerebral bridge (PB) reveals the absence of GABA from this neuropil. G: Schematic drawing of a sagittal section through the CB. Regions highlighted in gray contain GABA positive fibers (modified from [18], [21]. CBAL, anterior lip of the central body upper division; N, noduli. Scale bars = 100 µm in A; 50 µm in B; 40 µm in C; 20 µm in D, E and F.