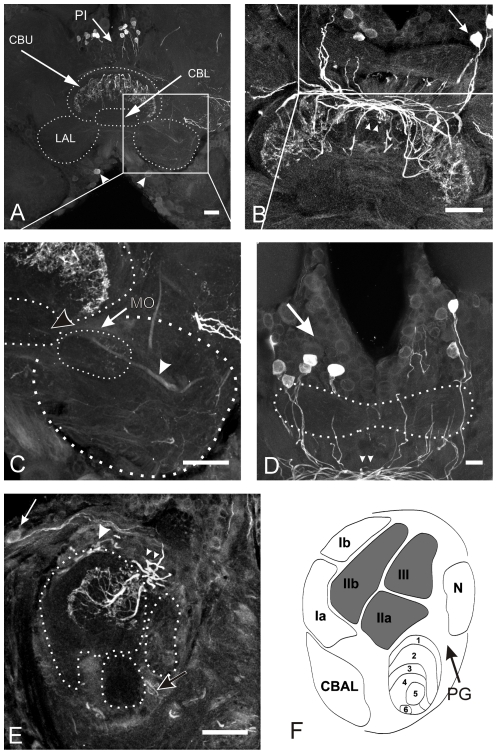
Figure 4. Citrulline immunoreactivity in the central complex.
A–D: Frontal sections through the midbrain and central complex. E: Sagittal section through the central complex. Groups of citrulline immunoreactive cell bodies are located in the pars intecerebralis (PI, white arrows in A, B, D and E) and in the inferior median protocerebrum (arrowheads in A). Citrulline immunoreactivity is restricted to the layers II and III of the upper division (CBU) of the central body, while layer I and the entire lower division (CBL) was completely free of immunostaining. Two types of immunoreactive neurons were distinguished. Pontine neurons contributing to intensive labeling in the posterior chiasm (small arrowheads in B, D and E) and additional faint labeling in tracts entering the CB through the dorsal and posterior face (large arrowhead in E). Immunostaining in the posterior groove (black arrow in E) resulted from tangential neurons. The lateral accessory lobes (LAL) contained weak staining. Citrulline-ir was detected in the median olive (MO in C) and the ventral shell (white arrowhead in C) of the LAL. F: Schematic drawing of a sagittal section through the CB (modified from [18], [21]. Regions highlighted in gray contain citrulline positive fibers. CBAL = anterior lip of the central body, N = noduli. Scale bars = 50 µm in A, B and C; 20 µm in D and E.