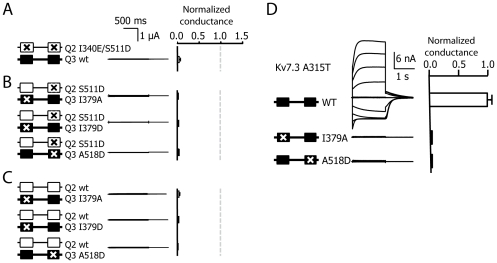
Figure 3. The S511D mutation did not restore the function of other CaM binding perturbing mutations.
Left column, schematic illustration of the CaM binding region as in Fig. 2. Kv7.2 subunits are represented by white boxes and Kv7.3 subunits by black boxes. Crosses indicate point mutations known to prevent CaM binding to Kv7.2 introduced at equivalent position in Kv7.2 or Kv7.3. Middle column, representative current recordings from Xenopus oocytes injected in a 1∶1 ratio of cRNAs for Kv7.3, Kv7.2, or the different mutants studied. Right column, normalized average conductance. Bars represent the mean ± SEM of the normalized conductance mutant Kv7.2/3 channels (n≥4). The dotted line is the reference normalized conductance from K7.2/3. A. The double mutant I340E/S511D Kv7.2 co-expressed with WT Kv7.3 was not functional. B. Introduction of CaM binding perturbing mutations in helix A or helix B of Kv7.3 lead to non-functional channels. Left, schematic representation of the mutants analyzed. Middle column, representative current traces of whole-cell patch-clamp recordings from HEK293T expressing homomeric Kv7.3T WT, I379A or A518D. The pore A315T mutation was introduced to boost expression [19]-[21]. C and D. Kv7.2 S511D or WT did not restore the function of Kv7.3 subunits carrying mutations in helix A or helix B. Currents were elicited with 800 ms jumps to potentials between -100 and +60 mV from a holding potential of -20 mV. Tail currents were measured at -20 mV. Right column, the difference in the amplitude of the relaxation measured at -20 mV after a pulse to -100 mV and +60 mV was measured (n≥8).