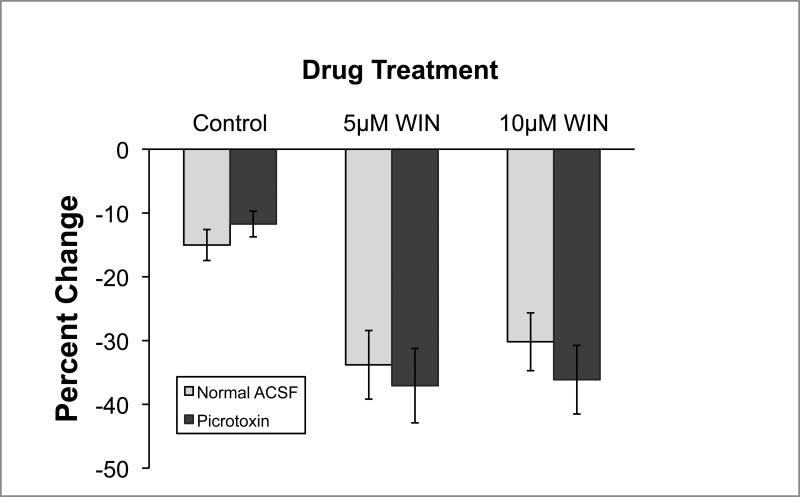
Figure 4.
Amplitude of the initial EPSC of a train is reduced by cannabinoid agonist both with and without blockade of GABAA receptors (n = 4-6 for each group). There was a slight reduction in the amplitude of the initial EPSC with the passage of time in control conditions. The percentage change in amplitude was much larger, however, when WIN 55,212-2 was bath applied during this time period. This effect appears to be at the glutamatergic auditory nerve – NM synapse since the WIN was equally effective when GABAA receptors were blocked with picrotoxin.