Figure 5.
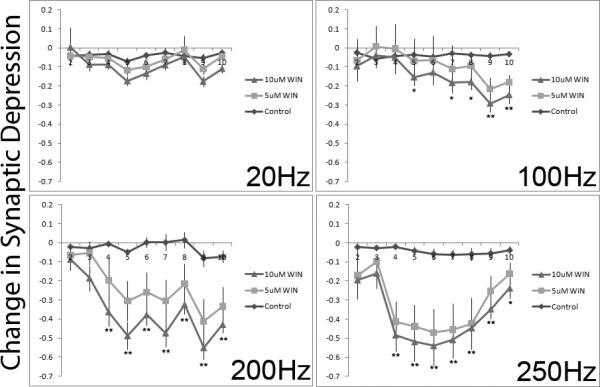
The CB1 agonist WIN 55,212-2 significantly reduces depression observed later in the pulse train when stimulated at high rates. Depression was measured across a train of 10 pulses before and after bath application of WIN. Amplitudes of EPSCs 2-10 were standardized to the amplitude of the 1st EPSC. The change in depression before and after WIN (standardized post-WIN amplitude – standardized pre-Win amplitude) administration is plotted by pulse number and separated by rate of stimulation. Lower numbers represent reduced depression after application of the CB1 agonist. Note that activation of the CB1 receptor reduced synaptic depression, particularly at the two highest rates of stimulation. Error bars represent standard error of the mean. N = 9-11 cells for each drug condition. ** indicates both WIN doses differ from control, * indicates only the high dose of WIN differs reliably from control.
