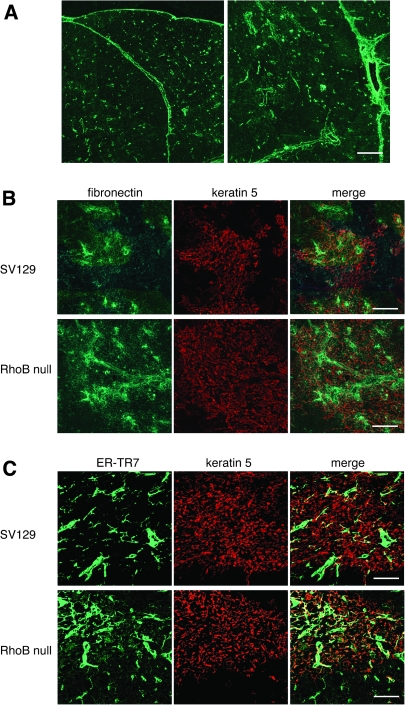
Fig. 5.
Lack of RhoB induces the increased expression of fibronectin in thymic medullary epithelium. (A) Expression of fibronectin in the thymus of adult mouse. Immunofluorescence staining of thymus sections of 6-week-old SV129 mice was performed to detect fibronectin. Fibronectin is detectable in the capsule, septa and perivascular cells. (B) Increased expression of fibronectin in thymic medullary region of RhoB-null mice. Immunofluorescence staining of thymus sections of 6-week-old male SV129 and RhoB-null thymus was performed to detect fibronectin (green) and keratin 5 (red). RhoB deficiency increases expression of fibronectin in thymic medullary region. Fibronectin associated with medullary epithelium is frequently seen. (C) Increased distribution of mesenchymal cells in thymic medullary region of RhoB-null mice. Thymus sections of 6-week-old SV129 and RhoB-null thymus were stained with ER-TR7 and anti-keratin 5 Ab. In RhoB-null thymus, accumulation of mesenchymal cells in thymic medullary region is frequently detectable. Data are representative of three independent experiments with six mice per group. Scale bars = 100 μm.