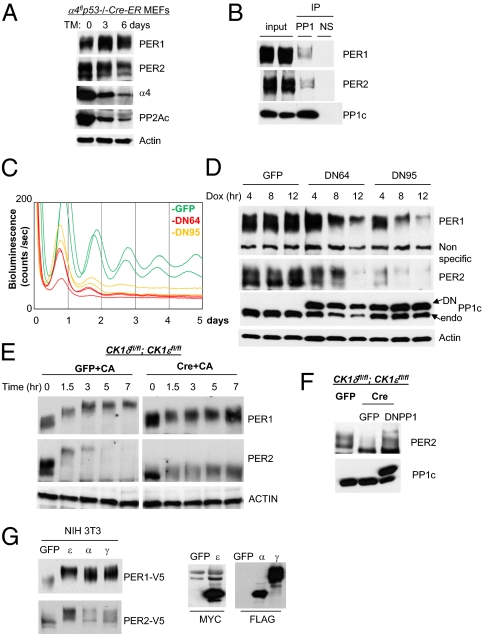
Fig. 4.
PP1 is a major PER phosphatase and essential for rhythm generation. (A) PP2Ac levels are dramatically reduced in α4 mutant fibroblasts, but PER phosphorylation is intact. Cre (used for conditional deletion of floxed α4) was activated by addition of 4-hydroxytamoxifen (TM) to the medium. (B) Coimmunoprecipitation of PER with PP1 catalytic subunit PP1c. (C) Shortened and compromised bioluminescence rhythms in dominant negative PP1 (DN64 or DN95)-expressing cells. Adenoviral DN64, DN95, or gfp was infected into Per2Luc fibroblasts, and expression of DN was initiated by doxycycline. The period (measured from the first two peaks) of the bioluminescence rhythms was 3–4 h shorter in DN-expressing cells. GFP: n = 6; period (hr) = 23.9 ± 0.2; relative amplitude = 53.0 ± 3.3. DN64: n = 4; period = 20.0 ± 0.1; amplitude = 15.4 ± 2.9. DN95: n = 4; period = 21.1 ± 0.1; amplitude = 26.5 ± 3.6. Values presented are mean ± SEM from three experiments. (D) Hyperphosphorylation and rapid degradation of PER induced by DN expression. Desynchronized cells were infected with adenovirus, treated with doxycycline, and harvested at the indicated times. (E) PER2 phosphorylation after CA treatment in CK1δ/ε-deficient cells. The mutant cells were harvested at the indicated times after CA treatment. (F) PER2 phosphorylation in the mutant cells with and without expression of DN64 (DNPP1). (G) PER phosphorylation by CK1α/γ in vitro. The kinases and Per were cotransfected into NIH 3T3 cells and harvested 48 h later. ε, CK1ε; α, CK1α; γ, CK1γ.