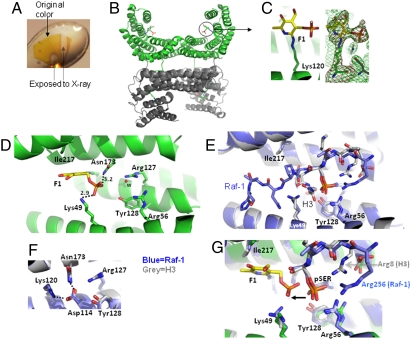
Fig. 2.
Structure of the 14-3-3ζ/F1 fragment covalent complex (A) Example color change of the 14-3-3ζ/F1 crystal after exposure to X-rays. (B) Two dimers of 14-3-3ζ in the asymmetric unit. (C) Covalently modified Lys120 in the peptide-binding groove of 14-3-3ζ. Omit electron densities, Fo-Fc (red mesh) and 2Fo-Fc (green mesh), contoured at 4σ and 1.2σ above the mean, respectively, are shown for F1-modified Lys120. (D) Details of 14-3-3ζ and F1 fragment interactions. The letter w indicates a solvent [either water in molecule (A-C) or a partially occupied phosphate in molecule (D)]. (E) Superimposition of 14-3-3ζ in complex with a Raf-1 peptide (blue) (PDB 3CU8) and a histone H3 peptide (gray) (PDB 2C1N). For clarity, H3 residues 12–14 (which point toward the viewer) were removed. (F) Lys120 is involved in intramolecular interactions. (G) Superimposition of a covalently bound F1 fragment (yellow) with that of Raf-1 (blue) and H3 (gray) phosphoserine peptides.