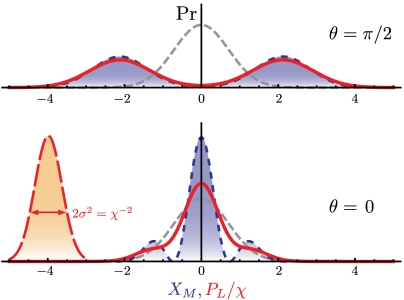
Fig. 2.
The scheme presented here provides an experimentally feasible means to obtain direct access to the marginals of a quantum state of a mechanical resonator. Shown are complementary quadrature marginals of the mechanical coherent state superposition 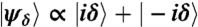 , for δ = 1.5 (blue dashed lines with fill, plotted with XM). The mechanical ground state is shown for comparison in gray dashed lines. The two population components are seen for the quadrature angle θ = π/2 and the quantum interference fringes for θ = 0. A coherent optical pulse is used to probe the mechanical state where its phase quadrature becomes the convolution between the intrinsic phase noise, with variance scaling with χ-2, and the mechanical marginal (red solid lines, plotted with PL/χ where χ = 2), see Eq. 4. The convolution kernel can be observed by using a fixed length cavity, shown in the θ = 0 plot (red dashed line with fill, fixed length with XM = -4), which allows for accurate recovery of the mechanical marginals even for a weak measurement strength χ.
, for δ = 1.5 (blue dashed lines with fill, plotted with XM). The mechanical ground state is shown for comparison in gray dashed lines. The two population components are seen for the quadrature angle θ = π/2 and the quantum interference fringes for θ = 0. A coherent optical pulse is used to probe the mechanical state where its phase quadrature becomes the convolution between the intrinsic phase noise, with variance scaling with χ-2, and the mechanical marginal (red solid lines, plotted with PL/χ where χ = 2), see Eq. 4. The convolution kernel can be observed by using a fixed length cavity, shown in the θ = 0 plot (red dashed line with fill, fixed length with XM = -4), which allows for accurate recovery of the mechanical marginals even for a weak measurement strength χ.