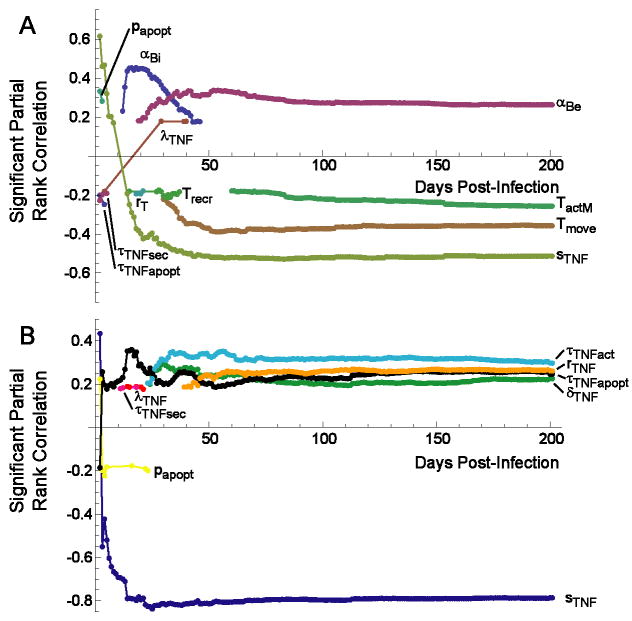
Figure 4.
Correlation of mechanisms in the model with extracelluar bacterial load over the course of infection. Graphs depict significant partial rank correlations (p < 0.01). A. Global sensitivity analysis reveals four dominant parameters. B. TNF-focused sensitivity analysis predicts the contribution of individual TNF-related mechanisms over time. Non-TNF parameters are set equal to the baseline control scenario (Tables 1-3) in panel B. αBe: extracellular Mtb growth rate; αBi: intracellular Mtb growth rate; papopt: probability of TNF-induced apoptosis in one ten-minute interval; Tmove: probability of T cell movement onto an occupied location; sTNF: rate of TNF secretion by macrophages; τTNFact: threshold for TNF-induced activation by macrophages; rMTNF: effect of TNF on trans-endothelial migration; δTNF: rate of TNF degradation; τTNFapopt: threshold for TNF-induced apoptosis by macrophages.