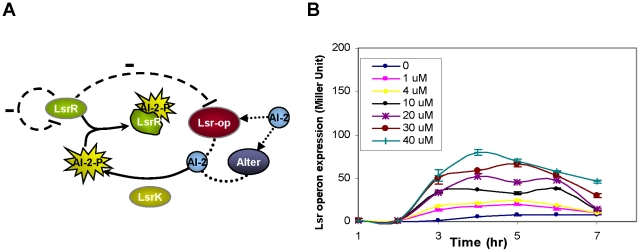
Figure 2. The AI-2 uptake mechanism.
A) The previously proposed network architecture of the AI-2 uptake is depicted. AI-2 is transported back into the cell through the transporter Lsr-operon and an unknown mechanism denoted “Alter”. Once AI-2 is inside the cell, it is phosphorylated by LsrK and the phosphorylated AI-2 (AI-2-P) interacts with the LsrR repressor. LsrR is a negative regulator that inhibits both the transcription of the lsr-operon and its own. AI-2-P can bind the LsrR protein and prevent the inhibition of the lsr-operon promoter. An increase in the levels of the Lsr transporter creates a positive feedback loop where higher concentrations of AI-2 within the cell result in an increase in AI-2 uptake. B) Temporal expression levels of the lsr-operon promoter for various concentrations of AI-2 ranging from 0 to 40 µM in luxS knock-out strains. Higher AI-2 concentrations result in higher expression rates from the lsr-operon. As the cells reach the stationary phase, the expression levels decrease for all doses.