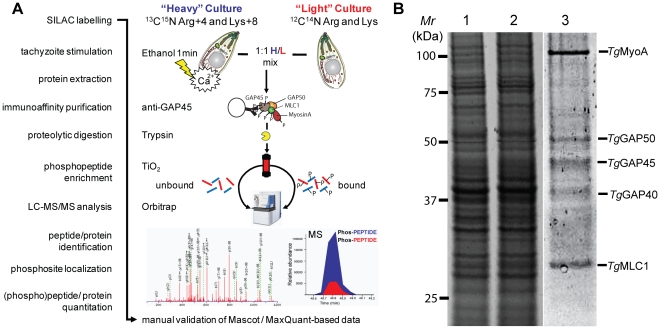
Figure 3. Quantification of calcium-dependent regulation of phosphorylation sites of Toxoplasma invasion motor complex components.
A) Work flow to identify individual phosphorylation sites and quantitatively assess their responsiveness to calcium signals using a SILAC-based proteomics approach. A 1∶1 mixture of Triton X-100 lysates from “Heavy” (H; Arg4/Lys8)-labeled ethanol-stimulated tachyzoites or "Light" (L; Arg0/Lys0)-labeled non-stimulated parasites was generated, and a TiO2-enriched phosphopeptide sample of H/L-labeled Toxoplasma invasion motor complexes was prepared and analysed by LC-MS/MS on an LTQ-Orbitrap instrument. Mascot and MaxQuant search engines facilitated subsequent manual identification, phosphosite localization and quantification of proteins or peptides as detailed in materials and mathods. B) Sypro Ruby-stained SDS-PAGE separation of the relative amounts of light (lane 1) or heavy (lane 2) Triton X-100 whole protein extracts are shown. Intact tachyzoite invasion motor complexes comprising the five major components MyoA, GAP50, GAP45 and MLC1 were precipitated from a 1∶1 H/L mixture by GAP45-specific immuno-affinity chromatography (lane 3).