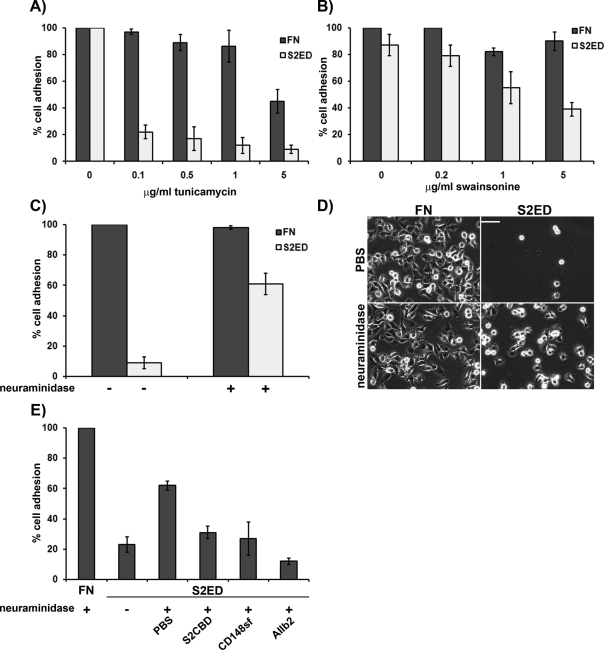
FIGURE 5:
Adhesion to S2ED is blocked by sialylation of cell surface receptors. Inhibitors of N-glycosylation, such as tunicamycin (A) and swainsonine (B), block rat embryo fibroblast cell adhesion to S2ED. Fibroblasts were seeded on wells coated with either FN (dark gray bars) or S2ED (light gray bars) for 60 min in the presence of either tunicamycin or swainsonine at the concentrations indicated. Adhesion is shown relative to cell adhesion to FN and S2ED in the absence of inhibitors, and error bars represent the SD of mean values of four replicates. Epithelial cells adhere to S2ED after treatment with neuraminidase (C). MDCK cells were seeded in serum-free media in the presence or absence of neuraminidase (500 U). Cells were incubated for 15 min at 37°C prior to seeding on wells coated with either FN (dark gray bars) or S2ED (light gray bars). Adhesion is shown relative to cell adhesion for untreated cells seeded on FN, and error bars are calculated as described in A and B. Phase-contrast micrographs of MDCK cells seeded on the substrates treated with either PBS or neuraminidase. Removal of sialic acid groups results in cell attachment and spreading. Scale bar, 50 μM. (E) HEK293 cells adhere to S2ED after treatment with neuraminidase, and the process is inhibited by S2CBD, CD148sf, and β1 integrin–blocking antibodies. Cells were seeded on the substrates indicated in serum-free media supplemented with neuraminidase and the S2 adhesion regulatory peptide S2CBD (25 μg/ml), CD148sf (20 μg/ml), or the β1 integrin–blocking antibody AIIb2 (10 μg/ml). Adhesion is calculated as a percentage of total cell adhesion to FN. Error bars represent the SD of five measurements.