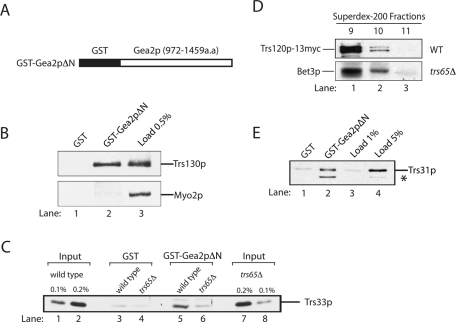
FIGURE 2:
The C-terminus of Gea2p binds to TRAPPII. (A) Amino acids 972–1459 of Gea2p (Gea2pΔN) were fused to GST and expressed in bacteria. (B) Trs130p binds to the C-terminus of Gea2p. Purified GST (lane 1) and GST-Gea2pΔN (lane 2) were immobilized on glutathione Sepharose beads and incubated with lysate. Lane 3 contains 0.5% of the lysate that was used in the binding reaction. (C) Trs65p is required for the interaction of TRAPPII with Gea2p. GST (lanes 3 and 4) and GST-Gea2pΔN beads (lanes 5 and 6) were incubated with lysates prepared from wild type or cells in which the genomic copy of TRS65 was disrupted. The beads were washed and solubilized, and the solubilized sample was electrophoresed on an SDS–PAGE. Wild-type (lanes 1 and 2) and trs65Δ (lanes 7 and 8) lysates used in the binding experiment were subjected to SDS–PAGE and blotted for Trs33p. (D) The TRAPPII complex is largely intact in trs65Δ cells. Superdex-200 column fractions 9–11 prepared from wild-type (top) and trs65Δ cells (bottom) were probed for Trs120p-13myc and Bet3p. (E) TRAPPII binds directly to the C-terminus of Gea2p. Purified GST (lane 1) and GST-Gea2pΔN (lane 2) were immobilized on glutathione Sepharose beads and incubated with purified TAP-tagged TRAPP (lanes 1 and 2). The beads were washed and solubilized, and the solubilized sample was electrophoresed on a 12% SDS–PAGE. The gel was probed with the indicated antibodies. Lanes 3 and 4 contain 1 and 5%, respectively, of the purified TRAPP that was added to the binding reaction. The asterisk marks a breakdown fragment of Trs31p.