FIGURE 1:
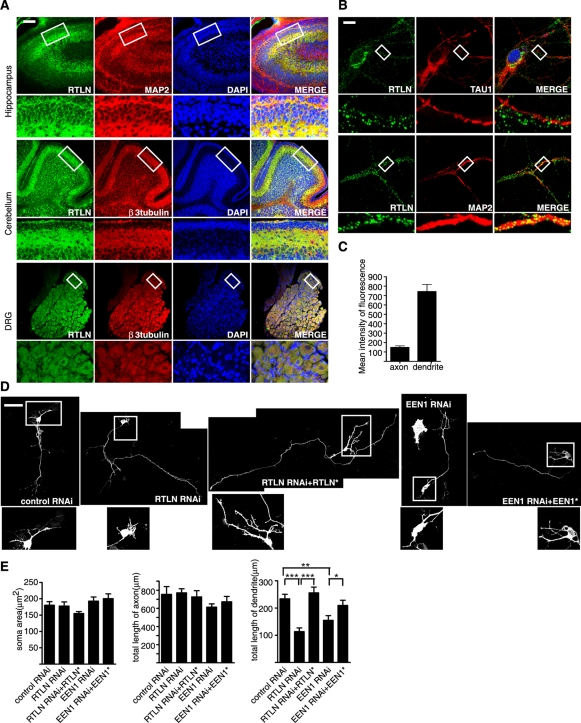
Retrolinkin is preferentially expressed in dendrites of CNS neurons and is required for dendrite outgrowth. (A) Immunohistochemical analysis of retrolinkin (labeled as RTLN) expression in the brain cortex, cerebellum, and dorsal root ganglia (DRG) of adult mouse. Regions within white boxes (top) are shown at higher magnification (bottom). Note that retrolinkin was strongly expressed in the dendrites of hippocampus and the molecular layer enriched of Purkinje cell dendrites in cerebellum. Scale bar, 100 μm. (B) Cultured hippocampal neurons were fixed and immunostained for endogenous retrolinkin (green) and the dendritic marker MAP2 (red) or the axonal marker TAU1 (red). Scale bar, 10 μm. (C) Background-subtracted, mean intensity of retrolinkin fluorescence in primary axons and dendrites. Measurement of fluorescence intensity is expressed in arbitrary units per square area in both axons and dendrites. All images were obtained in the same settings below saturation at a resolution of 1024 × 1024 pixels (12 bits) (n = 16; ***p < 0.001). (D) Hippocampal neurons were transfected at DIV1 with shRNA constructs coexpressing red fluorescent protein (RFP) and shRNA or cotransfected with shRNA and RNAi-resistant expression constructs (indicated by asterisk) and fixed at DIV5, followed by immunostaining with the anti-RFP antibody. Scale bar, 100 μm. (E) Quantification of soma area and neurite length per transfected neuron. Shown are average soma area (± SEM) and neurite length (± SEM) of 40–60 neurons (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01).