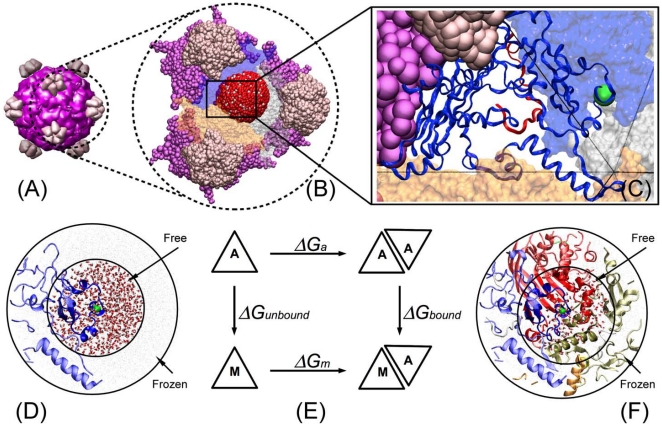
Figure 2. Interface mutations on the ID11 viral structure and design of the thermodynamic simulation model.
. (A) The mature virus capsid composed of 12 pentameric units. Each pentameric unit contains five identical copies of protein F (purple), and protein G (pink). (B) The simulation system containing three pentameric units. For each mutation a 35 Å radius sphere is defined to be centered on the mutation and is surrounded by water molecules and ions (red sphere). (C) Detailed view of one F protein and an example mutation (F314). (D) Representation of the left vertical path in thermodynamic cycle. A single protein in water is simulated. (E) Thermodynamic cycle. The horizontal paths are binding affinities that can be measured experimentally. In this study, the vertical paths are computed by thermodynamic integration. Because the binding affinity is a state function, the two vertical paths can be used to determine the relative binding affinity, i.e., ΔΔG = ΔGbound - ΔGunbound. (F) Representation of the right vertical path in thermodynamic cycle.