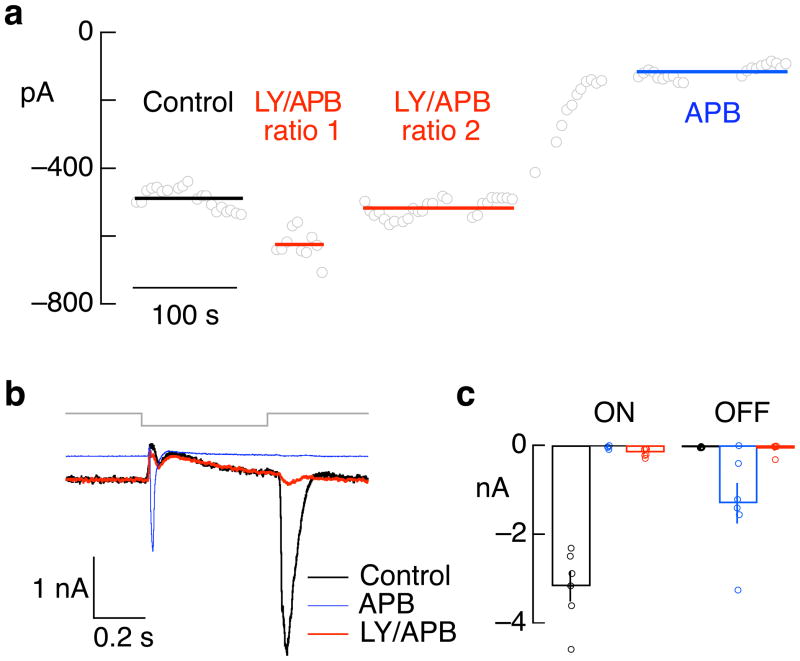
Figure 2.
Effect of APB and mixture of LY341495 and APB on light responses of ON parasol ganglion cells. a. Example of titration of mixture of LY341495 and APB to match the holding current without drugs. Open circles plot current in constant light (4000 R*/cone/sec) while holding the cell near the reversal potential for inhibitory synaptic input. The cell was superfused with solutions containing 7.5 μM LY341495 and 2.5 μM APB (ratio 1), 7.5 μM LY341495 and 5 μM APB (ratio 2) and 10 μM APB. b. Excitatory synaptic inputs to an ON parasol cell elicited by a decrement in light intensity from 4000 to 0 R*/cone/sec for 500 ms. Increases in light intensity generated large excitatory inputs in control conditions. APB decreased the holding current by suppressing tonic excitatory input, eliminated the response to increases in light intensity, and unmasked a large response to decreases in light intensity. A mixture of LY and APB almost entirely suppressed increases in excitatory input for both decreases and increases in light intensity while also matching the holding current in control conditions. Much of the current change remaining in LY/APB likely reflects OFF pathway derived presynaptic inhibition, which decreases bipolar cell glutamate release. c. Collected data from 6 cells as in a, plotting the maximum light-evoked inward current at light onset (ON) and offset (OFF).