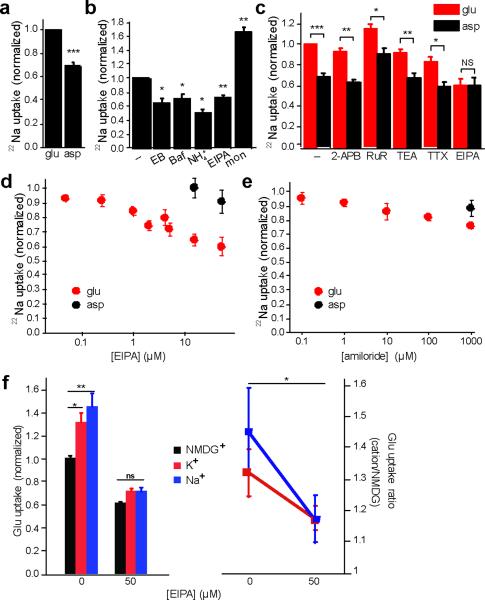
Figure 7. ΔpH-driven 22Na+ uptake into glutamatergic synaptic vesicles is EIPA-sensitive.
Synaptic vesicle uptake of 22Na+ was measured for 10 minutes in ATP and either 10 mM choline glutamate or 10 mM choline aspartate (a), and the results normalized to uptake in glutamate (n=25). (b) 22Na+ uptake was measured in the presence of ATP, glutamate and either EIPA (15 μM), Bafilomycin A1 (Baf) (0.5 μM), Evans Blue (EB) (100 μM), (NH4)2 tartrate (NH +4) (10 mM), or the Na+ ionophore monensin (mon) (5 μM) as positive control (n=3–5). (c) Uptake in 10 mM choline glutamate or aspartate, with and without 2-aminoethoxydiphenylborate (2-APB) (50 μM), ruthenium red (RuR) (100 μM), tetraethylammonium (TEA) (5 mM), tetrodotoxin (TTX) (0.5 μM) and EIPA (50 μM) (n=3–5). (d) EIPA inhibits 22Na+ uptake more potently in vesicles acidified with glutamate (n=3–6). (e) Amiloride also inhibits 22Na+ uptake, but less potently than EIPA (n=5–6). *, p < 0.05; **, p<0.01 and ***, p<0.0001; NS indicates p=0.99 by two-tailed paired t tests. (f) The uptake of 3H-glutamate was measured for 10 minutes in assay buffer containing 4 mM MgATP, 2 mM choline chloride, 10 mM glutamate, 10 mM NMDG gluconate and either 150 mM NMDG gluconate (black), 150 mM Na gluconate (blue) or 150 mM K gluconate (red), with or without EIPA. After subtraction of the background in 100 μM Evans Blue, uptake was normalized to that observed in NMDG gluconate without EIPA (left panel). The uptake in Na+ or K+ was then normalized to that in NMDG+ (right panel). *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01 by two-way ANOVA (n=15–18). Data indicate mean ± SEM.