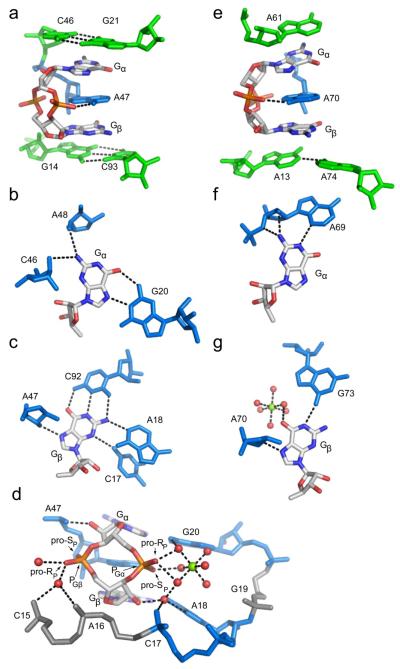
Figure 2.
c-di-GMP recognition by the class I and class II riboswitches. Coloring of RNA residues is the same as in Figure 1. c-di-GMP is colored by atom with carbon shown in white, oxygen in red, nitrogen in blue, and phosphorus in orange. Hydrogen bonds are shown as blacked dashed lines. (a) Side view of c-di-GMP bound to the class I aptamer. The G21-C46 base pair is the first base pair of the P2 helix and the G14-C93 base pair is the first of the P1 helix. A47 intercalates between Gα and Gβ. (b) Gα recognition and (c) Gβ recognition by the class I riboswitch. (d) Backbone recognition of c-di-GMP by the class I riboswitch. The phosphate 5′ of Gα (PGα) is more heavily contacted than the phosphate 5′ of Gβ (PGβ) and each ribose 2′-OH is involved in a single hydrogen bonding contact. PGα is coordinated by a magnesium ion, shown as a green sphere. Coordinated water molecules are shown as red spheres. (e) c-di-GMP is bound to the class II riboswitch in a similar conformation to class I, with adenosines stacking above (A61), below (A13 and A74), and in between (A70) Gα and Gβ. The hydrogen bond between the exocyclic amine of A70 and a non-bridging phosphate oxygen of c-di-GMP is the only backbone contact. (f) Interactions made by the class II aptamer to Gα and (g) Gβ.