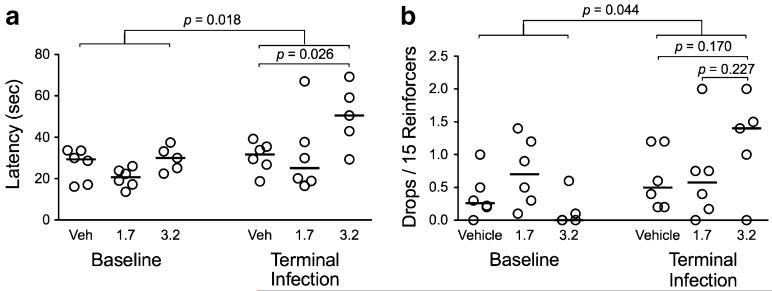
Fig. 7.
Bimanual motor skills task performance. Cocaine administered at the higher dose (3.2 mg/kg/day) were significantly slower to retrieve all 15 reinforcers and had a tendency to drop more reinforcers. The effect of cocaine and SIV were assessed by latency (a) and the number of reinforcers dropped (b) in the BMS task