Figure 2.
Model Fit and Behavior
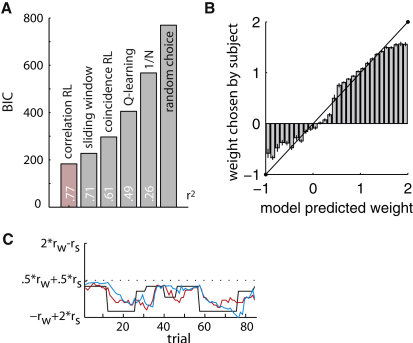
(A) The correlation learning model explained subjects' behavior best. Plotted are the Bayesian information criterions, which are corrected for the different levels of complexity in the models (smaller values are better). The r2 value represents the proportion of behavioral variance explained by each model.
(B) Regression of actual weights on model predicted weights. Data is pooled over all subjects; for single subject results see Table 1. Note that the deviations at the extremes are a result from bounding the possible weight range at −1 and 2; any behavioral errors at the boundary could therefore happen only in one direction. Error bars = SEM.
(C) Both the response of a representative subject (blue) and the model predicted weights (red) approach the normative best response under full knowledge of the generative correlation (black line) with some lag, which results from the time necessary to observe changes in correlation. Subjects responded after a 20-trial long observation-only phase (not shown).