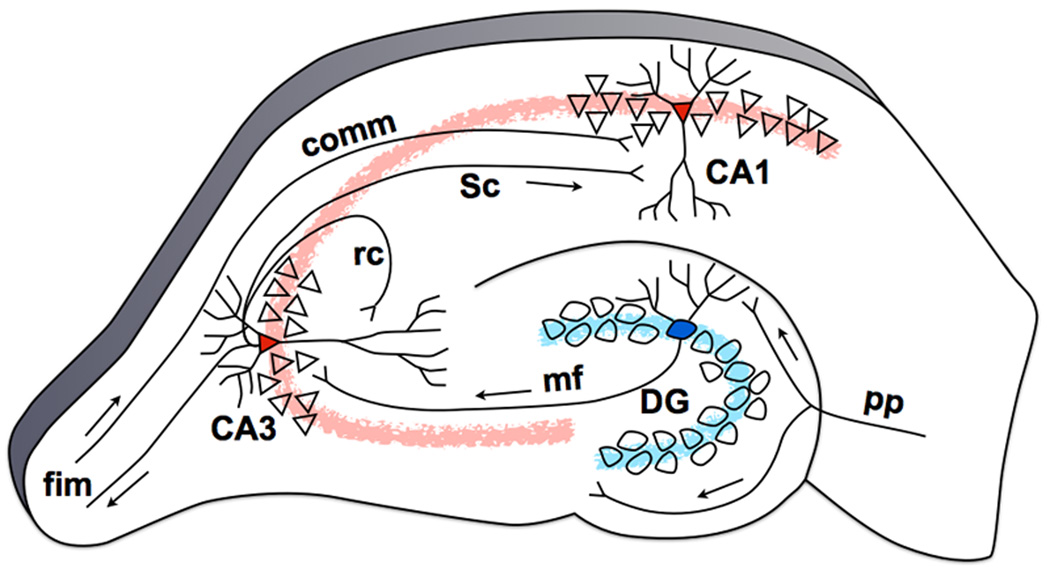
Figure 2. The hippocampal tri-synaptic circuit based on the rat brain.
Neurons in Layer II of the EC project to the DG, bypassing the subiculum, with additional collaterals projecting to the CA3 subfield (perforant path, pp). Granule cells in the DG project to the CA3 field of the hippocampus via the mossy fiber (mf) pathway. The CA3’s pyramidal cells project heavily onto themselves via recurrent collaterals (rc) and also to the CA1 through Schaffer collaterals (Sc). This trisynaptic circuit is a primarily feedforward circuit with very little feedback, except from the CA3 back to the DG via the hilar mossy cells [12] (not shown). The fimbria/fornix (fim) is one of the principal output pathways of the hippocampus that also brings in commissural (comm) input from the contralateral hippocampus.