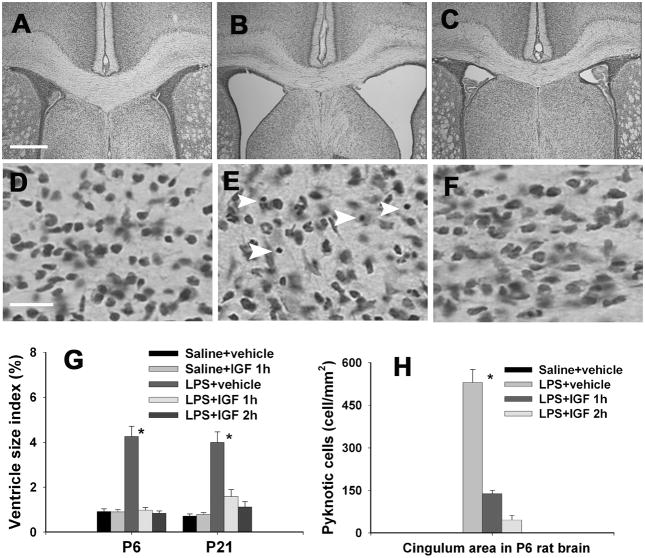
Figure 2.
Ventricle enlargement and the number of pyknotic cells in the cingulum area of the P6 or P21 rat brain. Intracerebral injection of LPS or sterile saline was performed in P5 rat pups and intranasal infusion of rhIGF-1or vehicle was performed 1 or 2 hr after the LPS injection. Nissl stained brain sections showed that perinatal LPS exposure resulted in a significant increase in ventricle size in the P6 rat brain (B) as compared to the control rat brain (A). Intranasal IGF-1 administration at 1 or 2 hr after LPS injection reduced dilatation of ventricles (C). Ventricle size index (area of the ventricles/area of whole brain sections at the bregma level) in the P6 and P21 rat brain is presented in G. Perinatal LPS exposure also significantly increased the number of pyknotic cells (indicated by white arrow heads) in the white matter area (E) and the cortical area 24 hr after the exposure. No pyknotic cells were detected in the saline-treated rat brain (D). Intranasal IGF-1 administration at 1 or 2 h after LPS injection reduced the number of pyknotic cells (F), as determined 24 hr after the LPS exposure. Quantitative data of pyknotic cells in the P6 rat brain are presented in H. * p<0.05 vs the other groups. Each group contained 6 animals. Scale bar: A–C, 500 μm; D–F, 20 μm.