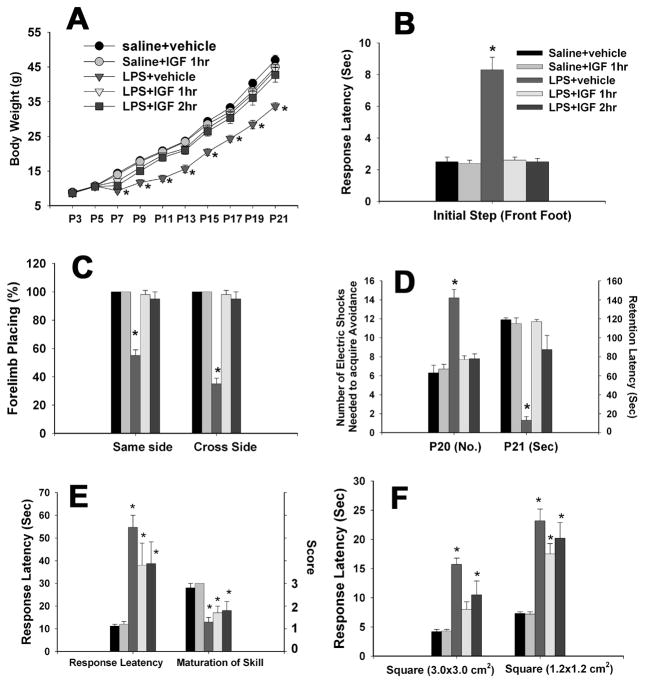
Figure 6.
Neurobehavioral tests following neonatal LPS exposure and IGF-1 treatment. Each group contained 6 animals. LPS exposure in P5 rats resulted in a significant body weight loss from P7 toP21 and administration of IGF-1 through intranasal infusion at either 1 or 2 hr after the LPS injection prevented LPS-induced weight loss (A). Neonatal LPS exposure also impaired the performance of P20 or P21 rats in the movement initiation test (B), the vibrissa-elicited forelimb-placing test (C) and the passive avoidance test (D). Intranasal infusion with rhIGF-1 at either 1 or 2 h after the LPS exposure reversed the LPS-induced impairment. *p<0.05 vs the other groups. Neonatal LPS exposure also impaired performance of rats in the pole test (E) and the bean walking test (F), but treatment with IGF-1did not improve performance in these two tests. *p<0.05 vs the saline+vehicle group in E and F.