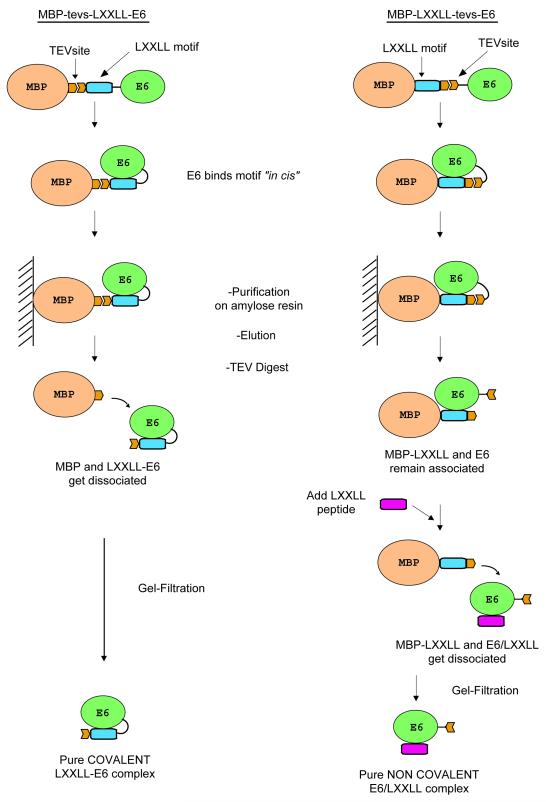
Fig. 3.
Purification scheme for the MBP-tevs-LXXLL-E6 construct (left) and the MBP-LXXLL-tevs-E6 construct (right). Both constructs stabilise the BPV1 E6 protein during expression by allowing it to form a complex in cis with its cognate LXXLL motif peptide. TEV digestion is carried out for both constructs after the first affinity purification step. In the case of the MBP-tevs-LXXLL-E6 construct, this leads to the isolation of pure covalent LXXLL-E6 complex after gel filtration. On the other hand, TEV proteolysis of the MBP-LXXLL-tevs-E6 construct is performed in the presence of a 4-fold excess of LXXLL synthetic peptide, which binds to the E6 moiety, allowing the displacement of the MBP-LXXLL fusion and leading to isolation of the non-covalent E6/LXXLL complex after gel filtration.