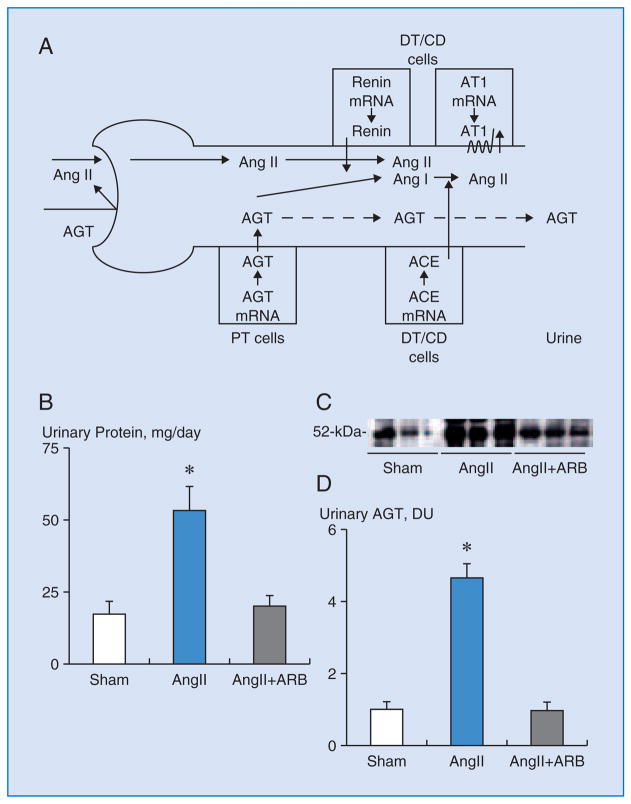
Figure 1.
Figure 1A. Intrarenal renin-angiotensin (Ang) system (RAS) in proximal and distal nephron segments 1. Because of its molecular size, it seems unlikely that much of the plasma angiotensinogen (AGT) filters across the glomerular membrane. In Ang II-dependent hypertension, increased proximal tubular (PT) secretion of AGT spills over into the distal nephron and increases Ang II effects on distal tubular (DT) reabsorption.
CD, collecting ducts. ACE, Ang converting enzyme. AT1, Ang II type 1 receptors.
Figures 1B – 1D. Urinary protein and AGT excretion rates of each group 38.
B. Urinary excretion rates of total protein were greater in Ang II-infused animals. ARB treatment prevented this augmentation.
C. Representative western blot analysis of urinary AGT levels among groups showing the stimulation in Ang II-infused group.
D. Urinary excretion rates of AGT were increased by 4.7-times in Ang II-infused animals. ARB treatment prevented this augmentation.
ARB, AT1 blocker. DU, densitometric units. *, p < 0.05 compared to the sham group.