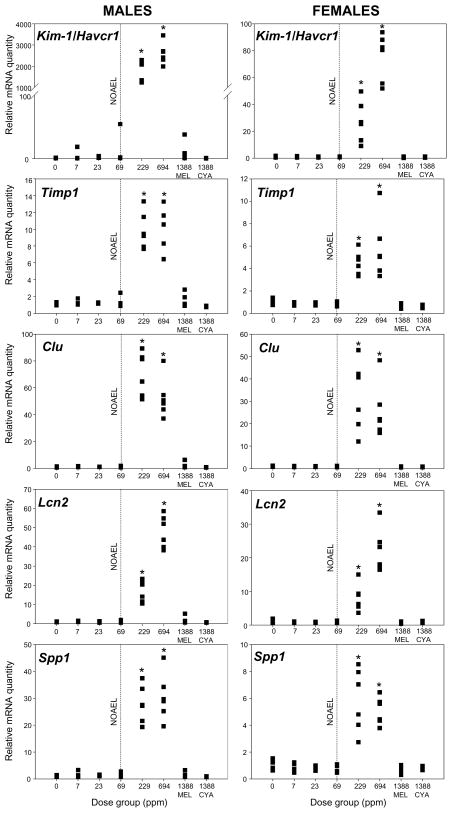
Figure 1.
Relative gene expression levels of biomarkers of nephrotoxicity (n = 6 per treatment group per sex) in kidneys of male and female F344 rats. Six-week-old animals were exposed to feed supplemented with 0 (control), 7, 23, 69, 229, or 694 ppm melamine and cyanuric acid (co-exposure groups), 1388 ppm melamine, or 1388 ppm cyanuric acid for seven days. Data were normalized for the endogenous control Gapdh and for the mean expression level of the matching (same sex) control by the ΔΔCt method; the control mean expression was normalized to 1. Left panel: male rats, right panel: female rats. Dashed line indicates the NOAEL as determined in Jacob et al. (2011). * indicates a significant group difference relative to the matching control (p-value < 0.05, one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test). All genes analyzed were significantly up-regulated in both male and female rats at dose levels higher than 69 ppm combined melamine and cyanuric acid.