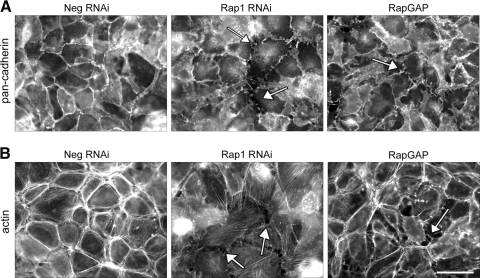
Figure 5.
Loss of Rap1 protein by knockdown or inhibition of Rap1 activity by expression of RapGAP disrupts cadherin and F-actin localization in ARPE-19 monolayers. ARPE-19 cells infected with the indicated RNAi viruses (Neg, Rap1), or RapGAPexpressing virus (RapGAP) were grown for 2 days and then replated onto coverslips for another 24 hours before fixation and processing for immunofluorescence microscopy. (A) Loss of Rap1 protein by knockdown or inhibition of its activity by RapGAP expression disrupts junctional localization of cadherins when compared with control (Neg) cells. The cell monolayer exhibits discontinuous cadherin staining and loss of cell-cell contact, producing gaps (examples indicated by arrows) in the normally confluent monolayer. (B) Knockdown of Rap1 or expression of RapGAP cause changes in morphology of the F-actin cytoskeleton. In control monolayers (Neg) actin staining is present in a perijunctional ring, however, knockdown of Rap1 results in the formation of cytoplasmic stress fibers and cell retraction, similar to expression of RapGAP. Scale bar, 50 μm.