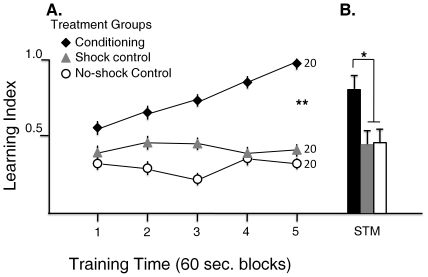
Figure 2. Learning and memory tests for bees in the groups for avoidance conditioning, none-shock control, and shock control.
The avoidance conditioning treatment served as the conditioning control in other experiments where influence of biogenic amines on learning and memory were tested. A. Learning: Bees in the avoidance conditioning group demonstrate a significant learning effect as indicated by increase in learning index over the 5 minute training period. This is in contrast to the none-shock and shock control groups with no evidence of improved avoidance where either no shock was applied or shock was applied to both halves of the apparatus. In repeated measures MANOVA, the conditioning group vs the control groups are significantly different (F = 11.09, df = 2, P<0.001). The change in learning index over time showed significant difference based on group (Repated measures MANOVA, time blocks (5) and groups (3) interaction: F = 2.28, df = 8, P<0.03). B. Short term memory (STM) test: In the STM test performed 20 minutes after the second training bout, the conditioning group bees scored high for learning index (mean ± SE = 0.80±0.09, N = 20) similar to the end of training period, and statistically significantly different than the control group bees ( none-shock control: mean ± SE = 0.46±0.1, N = 20; shock control mean ± SE = 0.44±0.1, N = 20; ANOVA for STM learning index: df = 2, F = 3.9, p<0.03).