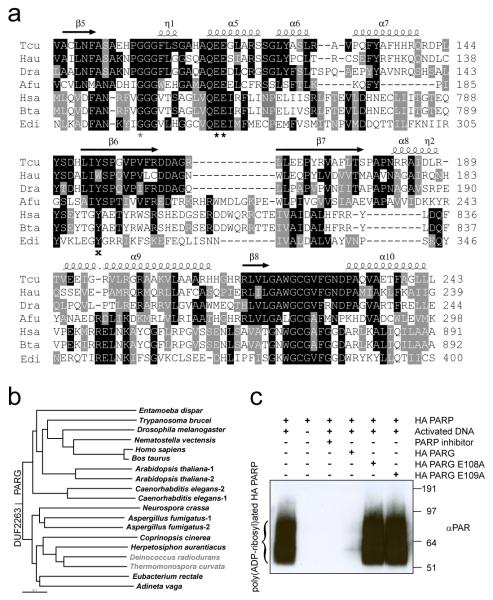
Figure 1. Phylogeny and functional relationship between DUF2263 and canonical-type PARGs.
a, Multiple sequence alignment of different DUF2263 and PARG proteins from Thermomonospora curvata (Tcu), Herpetosiphon aurantiacus (Hau), Deinococcus radiodurans (Dra), Aspergillus fumigatus (Afu), Homo sapiens (Hsa), Bos taurus (Bta) and Entamoeba dispar (Edi). The two catalytic glutamates, a conserved glycine and tyrosine are marked with black asterisks, grey asterisk and black cross respectively. Secondary structure elements from the Tcu PARG structure are indicated above. b, YmdB-rooted phylogenetic tree of PARGs implied by the neighbour-joining method. Organisms devoid of PARP are marked in grey. c, H. aurantiacus (HA) PARP and PARG enzymes are active as shown by Western blotting with anti-PAR antibodies.