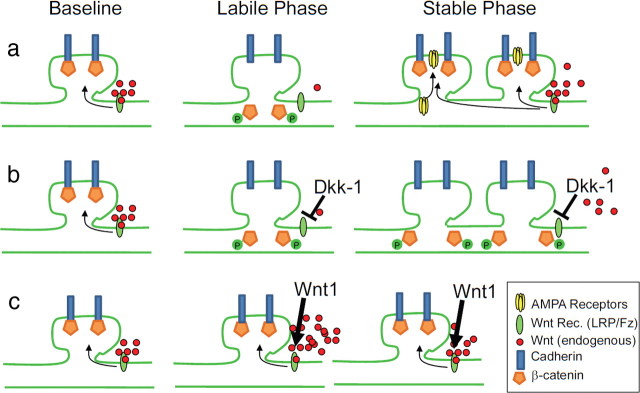
Figure 7.
Schematic representation of the role of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in producing the labile and stable phases of memory formation. a, Baseline levels of Wnt stabilize β-catenin/Cadherin synaptic stability, transient Wnt decrease during the labile phase allowing for synapse rearrangement, followed by Wnt normalization, which may mediate restabilization of newly formed synapses, which is also associated with increased AMPA trafficking and insertion (Rumpel et al., 2005; Yu et al., 2008; Migues et al., 2010; Nedelescu et al., 2010). b, In the presence of Dkk-1, restabilization does not occur, preventing normal memory consolidation. c, In the presence of Wnt1, the initial labile phase is prevented, also preventing normal memory consolidation.