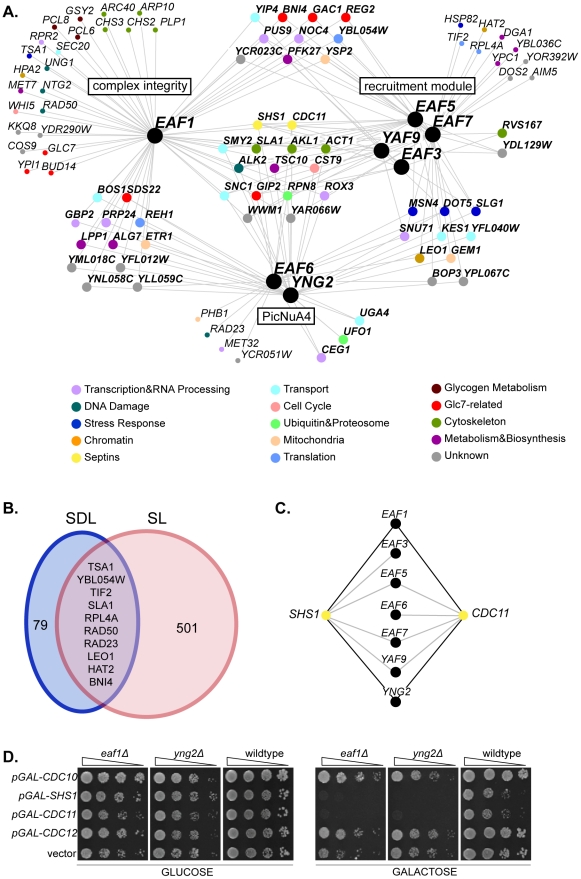
Figure 1. The NuA4 synthetic dosage lethal interaction network identifies a novel link with septin proteins.
(A) The NuA4 SDL genetic interaction network. Black nodes represent NuA4 genes, which are organized based on sub-complexes within the NuA4 complex (EAF1: complex integrity; EAF3, EAF5, EAF7, YAF9: recruitment module; EAF6, YNG2: Piccolo NuA4, PicNuA4). Interacting genes are represented by nodes colour-coded according to functional annotation as listed in the legend, and organized into groups based on the number of interactions with NuA4 sub-complexes. For instance, nodes located in the centre of the figure interact with one or more NuA4 mutants from each of the three sub-complexes. Small nodes denote genes that interact with only one NuA4 mutant. Edges indicate SDL or SDS genetic interactions (see also Table S3). (B) Comparison of the NuA4 SDL and SL genetic interactions identified by genome-wide screens for the five non-essential NuA4 subunits EAF1, EAF3, EAF5, EAF6, EAF7 (see Table S4 for the compiled list of SL interactions). (C) Overexpression of the septin genes CDC11 and SHS1 (yellow nodes) is toxic to most non-essential NuA4 deletion mutants (black nodes). Black and grey edges represent SDL or SDS interactions, respectively. (D) Overexpression of the septin genes CDC11 and SHS1 cause death in the absence of EAF1 or YNG2. Isogenic wild type (YKB779), eaf1Δ (YKB44) and yng2Δ (YKB494) cells containing galactose-inducible, plasmid-borne copy of galactose inducible CDC10, SHS1, CDC11, CDC12, or an empty vector control (pRS416) were spotted in serial ten-fold dilutions on minimal media lacking uracil and containing either glucose or galactose at 25°C for 3 or 5 days, respectively.